A Quantitative and Standardized Method for the Evaluation of Choroidal Neovascularization Using MICRON III Fluorescein Angiograms in Rats
- PMID: 26024231
- PMCID: PMC4449229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128418
A Quantitative and Standardized Method for the Evaluation of Choroidal Neovascularization Using MICRON III Fluorescein Angiograms in Rats
Abstract
Introduction: In-vivo imaging of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) has been increasingly recognized as a valuable tool in the investigation of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in both clinical and basic research applications. Arguably the most widely utilised model replicating AMD is laser generated CNV by rupture of Bruch's membrane in rodents. Heretofore CNV evaluation via in-vivo imaging techniques has been hamstrung by a lack of appropriate rodent fundus camera and a non-standardised analysis method. The aim of this study was to establish a simple, quantifiable method of fluorescein fundus angiogram (FFA) image analysis for CNV lesions.
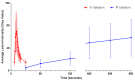
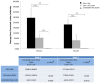
Methods: Laser was applied to 32 Brown Norway Rats; FFA images were taken using a rodent specific fundus camera (Micron III, Phoenix Laboratories) over 3 weeks and compared to conventional ex-vivo CNV assessment. FFA images acquired with fluorescein administered by intraperitoneal injection and intravenous injection were compared and shown to greatly influence lesion properties. Utilising commonly used software packages, FFA images were assessed for CNV and chorioretinal burns lesion area by manually outlining the maximum border of each lesion and normalising against the optic nerve head. Net fluorescence above background and derived value of area corrected lesion intensity were calculated.
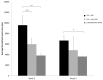
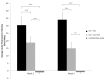
Results: CNV lesions of rats treated with anti-VEGF antibody were significantly smaller in normalised lesion area (p < 0.001) and fluorescent intensity (p < 0.001) than the PBS treated control two weeks post laser. The calculated area corrected lesion intensity was significantly smaller (p < 0.001) in anti-VEGF treated animals at 2 and 3 weeks post laser. The results obtained using FFA correlated with, and were confirmed by conventional lesion area measurements from isolectin stained choroidal flatmounts, where lesions of anti-VEGF treated rats were significantly smaller at 2 weeks (p = 0.049) and 3 weeks (p < 0.001) post laser.
Conclusion: The presented method of in-vivo FFA quantification of CNV, including acquisition variable corrections, using the Micron III system and common use software establishes a reliable method for detecting and quantifying CNV enabling longitudinal studies and represents an important alternative to conventional CNV quantification methods.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
-
Inhibition of experimental choroidal neovascularization in mice by anti-VEGFA/VEGFR2 or non-specific siRNA.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Sep;91(3):433-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.06.019. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20599960
-
A novel imaging technique for experimental choroidal neovascularization.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Dec;47(12):5163-70. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0156. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 17122098
-
A Simple Optical Coherence Tomography Quantification Method for Choroidal Neovascularization.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;31(8):447-54. doi: 10.1089/jop.2015.0049. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26060878 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models of Choroidal Neovascularization: A Systematic Review.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Aug 2;63(9):11. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.9.11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35943733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ApoM-bound S1P acts via endothelial S1PR1 to suppress choroidal neovascularization and vascular leakage.Angiogenesis. 2025 Apr 23;28(2):24. doi: 10.1007/s10456-025-09975-7. Angiogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40266369 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral delivered aflibercept OXB-203 for treatment of neovascular AMD.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023 Jul 15;30:350-366. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.07.001. eCollection 2023 Sep 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023. PMID: 37637380 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of retinal blood leakage in fundus fluorescein angiography in a retinal angiogenesis model.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 6;11(1):19903. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99434-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34615975 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Grading System for Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 18;11(7):2022. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11072022. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509662 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time OCT guidance and multimodal imaging monitoring of subretinal injection induced choroidal neovascularization in rabbit eyes.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Sep;186:107714. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107714. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31288022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman DS, O'Colmain BJ, Munoz B, Tomany SC, McCarty C, de Jong PT, et al. (2004) Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol 122: 564–572. - PubMed
-
- Zarbin MA (1998) Age-related macular degeneration: review of pathogenesis. Eur J Ophthalmol 8: 199–206. - PubMed
-
- Dobi ET, Puliafito CA, Destro M (1989) A new model of experimental choroidal neovascularization in the rat. Arch Ophthalmol 107: 264–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

