Long-term weight change: association with impaired glucose metabolism in young Austrian adults
- PMID: 26024372
- PMCID: PMC4449045
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127186
Long-term weight change: association with impaired glucose metabolism in young Austrian adults
Abstract
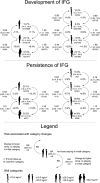
Little is known about the associations between long-term weight change and the natural history of impaired fasting glucose (IFG) in young adults. We investigated the association between long-term body mass index (BMI) change and the risk of IFG using data of 24,930 20- to 40-year-old participants from the Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Program (VHM&PP) cohort. Poisson models were applied to estimate the 10-year risk for new development of IFG (≥ 5.6 mmol/L), and persistence of IFG. Over 10 years, most men (68.2%) and women (70.0%) stayed within their initial BMI category. The risk for incident IFG was highest for men and women with persisting obesity (37.4% and 24.1%) and lowest with persisting normal weight (15.7% and 9.3%). Men transitioning from normal to overweight increased their risk of incident IFG by factor 1.45 (95%-CI: 1.31, 1.62), women by 1.70 (95%-CI: 1.50, 1.93), whereas transitioning from overweight to normal weight decreased the risk in men by 0.69 (95%-CI: 0.53, 0.90) and 0.94 (95%-CI: 0.66, 1.33) in women. Relative risks for men and women transitioning from obesity to overweight were 0.58 and 0.44, respectively. In conclusion, 10 year weight increase was associated with an increased IFG risk, weight decrease with a decreased risk of IFG in young adults.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between BMI and risk of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose in Chinese adults: a prospective study.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jan 3;23(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14912-0. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36597050 Free PMC article.
-
[Situation of impaired glucose regulation and metabolic syndrome in overweight or obesity adolescent students in Dongguan city].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Jun;43(6):495-500. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19950716 Chinese.
-
Synergistic effects of glucose tolerance and BMI on cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in a healthy population: CA.ME.LI.A study 7 years follow-up.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):E498-E511. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00181.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39196799 Free PMC article.
-
Prediabetes and its relationship with obesity in Mexican adults: The Mexican Diabetes Prevention (MexDiab) Study.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008 Mar;6(1):15-23. doi: 10.1089/met.2007.0020. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008. PMID: 18370832
-
Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in children and adolescents with overweight/obesity.J Endocrinol Invest. 2017 Apr;40(4):409-416. doi: 10.1007/s40618-016-0576-8. Epub 2016 Nov 16. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017. PMID: 27854028
Cited by
-
The Prevalence and Associated Factors of Impaired Fasting Glucose among Children and Adolescents in Urban China: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study.Pediatr Diabetes. 2024 Mar 15;2024:6701192. doi: 10.1155/2024/6701192. eCollection 2024. Pediatr Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 40302960 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass trajectories, diabetes mellitus, and mortality in a large cohort of Austrian adults.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Dec;95(49):e5608. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005608. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27930587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mensink GBM, Schienkiewitz A, Haftenberger M, Lampert T, Ziese T, Scheidt-Nave C. [Overweight and obesity in Germany: results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2013;56:786–94. 10.1007/s00103-012-1656-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peter RS, Fromm E, Klenk J, Concin H, Nagel G. Change in Height, Weight, and body mass index: Longitudinal data from Austria. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2014; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

