The Homeobox Genes of Caenorhabditis elegans and Insights into Their Spatio-Temporal Expression Dynamics during Embryogenesis
- PMID: 26024448
- PMCID: PMC4448998
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126947
The Homeobox Genes of Caenorhabditis elegans and Insights into Their Spatio-Temporal Expression Dynamics during Embryogenesis
Abstract
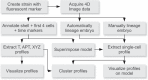
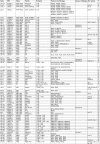
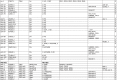
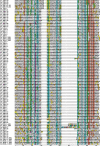
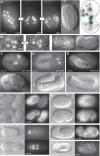
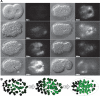
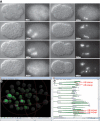
Homeobox genes play crucial roles for the development of multicellular eukaryotes. We have generated a revised list of all homeobox genes for Caenorhabditis elegans and provide a nomenclature for the previously unnamed ones. We show that, out of 103 homeobox genes, 70 are co-orthologous to human homeobox genes. 14 are highly divergent, lacking an obvious ortholog even in other Caenorhabditis species. One of these homeobox genes encodes 12 homeodomains, while three other highly divergent homeobox genes encode a novel type of double homeodomain, termed HOCHOB. To understand how transcription factors regulate cell fate during development, precise spatio-temporal expression data need to be obtained. Using a new imaging framework that we developed, Endrov, we have generated spatio-temporal expression profiles during embryogenesis of over 60 homeobox genes, as well as a number of other developmental control genes using GFP reporters. We used dynamic feedback during recording to automatically adjust the camera exposure time in order to increase the dynamic range beyond the limitations of the camera. We have applied the new framework to examine homeobox gene expression patterns and provide an analysis of these patterns. The methods we developed to analyze and quantify expression data are not only suitable for C. elegans, but can be applied to other model systems or even to tissue culture systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
CeRh1 (rhr-1) is a dominant Rhesus gene essential for embryonic development and hypodermal function in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 11;103(15):5881-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600901103. Epub 2006 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16595629 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic axial patterning requires two recently discovered posterior-group Hox genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4499-503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.9.4499. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10781051 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ectodermal and excretory function by the C. elegans POU homeobox gene ceh-6.Development. 2001 Mar;128(5):779-90. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.5.779. Development. 2001. PMID: 11171402
-
Aggrephagy: lessons from C. elegans.Biochem J. 2013 Jun 15;452(3):381-90. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121721. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23725457 Review.
-
Homeobox genes in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):275-7. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90034-m. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993. PMID: 8099297 Review.
Cited by
-
An insight into the functional genomics and species classification of Eudiplozoon nipponicum (Monogenea, Diplozoidae), a haematophagous parasite of the common carp Cyprinus carpio.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jun 29;24(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09461-8. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37380941 Free PMC article.
-
How Weird is The Worm? Evolution of the Developmental Gene Toolkit in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Dev Biol. 2019 Sep 28;7(4):19. doi: 10.3390/jdb7040019. J Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31569401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Series of Tubes: The C. elegans Excretory Canal Cell as a Model for Tubule Development.J Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 7;8(3):17. doi: 10.3390/jdb8030017. J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32906663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The homeodomain transcription factor CEH-37 regulates PMK-1/p38 MAPK pathway to protect against intestinal infection via the phosphatase VHP-1.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Oct 5;80(11):312. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04970-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37796333 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of distinct syntenic density regimes is associated with early metazoan genomic transitions.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 17;23(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08304-2. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35177000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruvkun G, Hobert O. The taxonomy of developmental control in Caenorhabditis elegans . Science (New York, NY). 1998;282:2033–41. - PubMed
-
- Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR. C. elegans II Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. 1222 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

