1H HR-MAS NMR Based Metabolic Profiling of Cells in Response to Treatment with a Hexacationic Ruthenium Metallaprism as Potential Anticancer Drug
- PMID: 26024484
- PMCID: PMC4449131
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128478
1H HR-MAS NMR Based Metabolic Profiling of Cells in Response to Treatment with a Hexacationic Ruthenium Metallaprism as Potential Anticancer Drug
Abstract
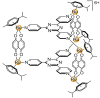
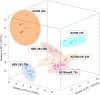
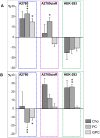
(1)H high resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy was applied in combination with multivariate statistical analyses to study the metabolic response of whole cells to the treatment with a hexacationic ruthenium metallaprism [1](6+) as potential anticancer drug. Human ovarian cancer cells (A2780), the corresponding cisplatin resistant cells (A2780cisR), and human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293) were each incubated for 24 h and 72 h with [1](6+) and compared to untreated cells. Different responses were obtained depending on the cell type and incubation time. Most pronounced changes were found for lipids, choline containing compounds, glutamate and glutathione, nucleotide sugars, lactate, and some amino acids. Possible contributions of these metabolites to physiologic processes are discussed. The time-dependent metabolic response patterns suggest that A2780 cells on one hand and HEK-293 cells and A2780cisR cells on the other hand may follow different cell death pathways and exist in different temporal stages thereof.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Rosenberg B, Vancamp L, Krigas T. Inhibition of Cell Division in Escherichia Coli by Electrolysis Products from A Platinum Electrode. Nature 1965;205: 698–699. - PubMed
-
- Keppler BK, Rupp W, Juhl UM, Endres H, Niebl R, Balzer W. Synthesis, molecular structure, and tumor-inhibiting properties of imidazolium trans-bis(imidazole)tetrachlororuthenate(III) and its methyl-substituted derivatives. Inorg Chem. 1987;26: 4366–4370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

