The Effects of Estrogen Receptors' Antagonist on Brain Edema, Intracranial Pressure and Neurological Outcomes after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rat
- PMID: 26024665
- PMCID: PMC4571012
- DOI: 10.7508/ibj.2015.03.006
The Effects of Estrogen Receptors' Antagonist on Brain Edema, Intracranial Pressure and Neurological Outcomes after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rat
Abstract
Background: In previous studies, the neuroprotective effect of 17β-estradiol in diffuse traumatic brain injury has been shown. This study used ICI 182,780, a non-selective estrogen receptor antagonist, to test the hypothesis that the neuroprotective effect of 17β-estradiol in traumatic brain injury is mediated by the estrogen receptors.
Methods: The ovariectomized rats were divided into eight groups. Brain injury was induced by Marmarou's method. Estrogen was injected 30 minutes after traumatic brain injury, and ICI 182,780 was injected before traumatic brain injury and also before estrogen treatment. In one group only ICI 182,780 was injected. The brain water content and Evans blue dye content were measured 24 and 5 hours after traumatic brain injury, respectively. The neurologic outcomes and intracranial pressure were assessed before, 4, and 24 hours after traumatic brain injury.
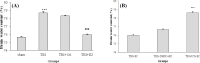
Results: Brain water content and Evans blue content were less in estrogen-treated group comparison to vehicle group. ICI 182,780 eliminated the effects of estrogen on brain edema and brain blood barrier permeability. Intracranial pressure was increased significantly after trauma, and estrogen decreased intracranial pressure at 4 and 24 hours after traumatic brain injury in comparison to vehicle. This inhibitory effect was also eliminated by treatment with ICI182,780. ICI 182,780 also inhibited the estrogen induced increase in neurologic outcomes following traumatic brain injury. However, the use of ICI 182,780 alone had no neuroprotective effect after traumatic brain injury.
Conclusion: The results suggest that classical estrogen receptors have probably a role in the neuroprotective function of estrogen following traumatic brain injury.
Keywords: Brain edema; Estrogens; Intracranial pressure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The brain cytokine levels are modulated by estrogen following traumatic brain injury: Which estrogen receptor serves as modulator?Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):279-87. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.046. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26112336
-
E2-BSA and G1 exert neuroprotective effects and improve behavioral abnormalities following traumatic brain injury: The role of classic and non-classic estrogen receptors.Brain Res. 2021 Jan 1;1750:147168. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147168. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33096091
-
Effect of sex steroid hormones on brain edema, intracranial pressure, and neurologic outcomes after traumatic brain injury.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;88(4):414-21. doi: 10.1139/y09-126. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20555409
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction following traumatic brain injury.Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Oct;30(5):1093-104. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9651-7. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2015. PMID: 25624154 Review.
-
Substance P antagonists as a novel intervention for brain edema and raised intracranial pressure.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2013;118:201-4. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1434-6_37. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2013. PMID: 23564132 Review.
Cited by
-
The anti-inflammatory properties of Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad essential oil attenuate the effects of traumatic brain injuries in rats.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 18;6:31866. doi: 10.1038/srep31866. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27535591 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-related responses after traumatic brain injury: Considerations for preclinical modeling.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018 Jul;50:52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 May 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29753798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Female Sex Steroids Administration on Pathophysiologic Mechanisms in Traumatic Brain Injury.Transl Stroke Res. 2018 Aug;9(4):393-416. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0588-5. Epub 2017 Nov 19. Transl Stroke Res. 2018. PMID: 29151229 Review.
References
-
- Mota BC, Pereira L, Souza MA, Silva LFA, Magni DV, Ferreira APO, et al. Exercise pre-conditioning reduces brain inflammation and protects against toxicity induced by traumatic brain injury: behavioral and neurochemical approach. Neurotox Res. 2012 Feb;21(2):175–84. - PubMed
-
- Urban RJ. Hypopituitarism after acute brain injury. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2006 Jul;16:25–9. - PubMed
-
- Dang J, Mitkari B, Kipp M, Beyer C. Gonadal steroids prevent cell damage and stimulate behavioral recovery after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in male and female rats. Brain Behav Immun. 2011 May;25(4):715–26. - PubMed
-
- Shahrokhi N, Khaksari M, Soltani Z, Mahmoodi M, Nakhaee N. Effect of sex steroid hormones on brain edema, intracranial pressure, and neurologic outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;88(4):414–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
