Quinine Bitterness and Grapefruit Liking Associate with Allelic Variants in TAS2R31
- PMID: 26024668
- PMCID: PMC4542653
- DOI: 10.1093/chemse/bjv027
Quinine Bitterness and Grapefruit Liking Associate with Allelic Variants in TAS2R31
Abstract
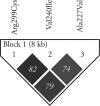
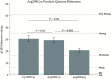
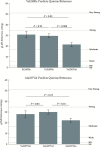
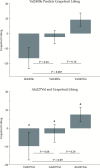
Multiple psychophysical gene-association studies suggest a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within the bitter receptor gene TAS2R19 on chromosome 12 may be functional. Previously, the Arg299Cys SNP (rs10772420) has been associated with differential bitterness of quinine and differential liking for grapefruit juice. However, quinine does not activate TAS2R19 in vitro; likewise, limonin and naringin, bitter compounds in grapefruit, do not activate TAS2R19 in vitro. Here, we examined quinine bitterness (whole-mouth swish-and-spit stimuli and regionally delivered quinine across 4 loci) and remembered liking for grapefruit juice to test whether they associate with SNPs in another nearby gene, TASR2R31. We observed SNP-phenotype associations between whole-mouth quinine bitterness and self-reported liking for grapefruit juice with SNPs in TAS2R31, and regional quinine bitterness followed a similar trend, but did not reach significance. Present data provide independent replication of prior associations reported for TAS2R19. However, we also observed strong linkage disequilibrium (LD) between TAS2R19 and TAS2R31 SNPs. When present data are considered in light of existing functional expression data, this suggests phenotypic associations reported previously for rs10772420 may potentially be due to LD between this SNP and polymorphism(s) in, or closer to, TAS2R31. If confirmed, this would reduce the number of TAS2Rs with putatively functional polymorphisms to 5.
Keywords: Project GIANT-CS; bitter receptors; bitterness; direct scaling; false positive; linkage disequilibrium (LD); psychophysics; taste.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allelic variation in TAS2R bitter receptor genes associates with variation in sensations from and ingestive behaviors toward common bitter beverages in adults.Chem Senses. 2011 Mar;36(3):311-9. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjq132. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Chem Senses. 2011. PMID: 21163912 Free PMC article.
-
Bitterness of the non-nutritive sweetener acesulfame potassium varies with polymorphisms in TAS2R9 and TAS2R31.Chem Senses. 2013 Jun;38(5):379-89. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt017. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Chem Senses. 2013. PMID: 23599216 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in TRPV1 and TAS2Rs associate with sensations from sampled ethanol.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Oct;38(10):2550-60. doi: 10.1111/acer.12527. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25257701 Free PMC article.
-
Bitter flavors and bitter compounds in foods: identification, perception, and reduction techniques.Food Res Int. 2024 May;183:114234. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114234. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38760147 Review.
-
Research progress of the bitter taste receptor genes in primates.Yi Chuan. 2018 Feb 20;40(2):126-134. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-258. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 29428905 Review.
Cited by
-
Bitter taste receptors: Genes, evolution and health.Evol Med Public Health. 2021 Oct 13;9(1):431-447. doi: 10.1093/emph/eoab031. eCollection 2021. Evol Med Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35154779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of sweet, umami, and bitter taste receptor (TAS1R and TAS2R) genomic and expression alterations in solid tumors on survival.Sci Rep. 2022 May 27;12(1):8937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12788-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35624283 Free PMC article.
-
Differential bitterness in capsaicin, piperine, and ethanol associates with polymorphisms in multiple bitter taste receptor genes.Physiol Behav. 2016 Mar 15;156:117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26785164 Free PMC article.
-
Chemosensory Changes from Cancer Treatment and Their Effects on Patients' Food Behavior: A Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 24;11(10):2285. doi: 10.3390/nu11102285. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31554217 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and improving the sensory and hedonic responses to polyphenol-rich aronia berry juice.Appetite. 2016 Dec 1;107:116-125. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2016.07.026. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Appetite. 2016. PMID: 27457970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balding DJ. 2006. A tutorial on statistical methods for population association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 7:781–791. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. 2005. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 21:263–265. - PubMed
-
- Bartoshuk LM, Duffy VB, Green BG, Hoffman HJ, Ko CW, Lucchina LA, Marks LE, Snyder DJ, Weiffenbach JM. 2004. Valid across-group comparisons with labeled scales: the gLMS versus magnitude matching. Physiol Behav. 82:109–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

