Neural control of circulation and exercise: a translational approach disclosing interactions between central command, arterial baroreflex, and muscle metaboreflex
- PMID: 26024683
- PMCID: PMC4631530
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00077.2015
Neural control of circulation and exercise: a translational approach disclosing interactions between central command, arterial baroreflex, and muscle metaboreflex
Abstract
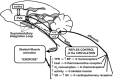
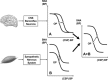
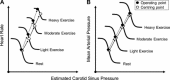
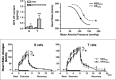
The last 100 years witnessed a rapid and progressive development of the body of knowledge concerning the neural control of the cardiovascular system in health and disease. The understanding of the complexity and the relevance of the neuroregulatory system continues to evolve and as a result raises new questions. The purpose of this review is to articulate results from studies involving experimental models in animals as well as in humans concerning the interaction between the neural mechanisms mediating the hemodynamic responses during exercise. The review describes the arterial baroreflex, the pivotal mechanism controlling mean arterial blood pressure and its fluctuations along with the two main activation mechanisms to exercise: central command (parallel activation of central somatomotor and autonomic descending pathways) and the muscle metaboreflex, the metabolic component of exercise pressor reflex (feedback from ergoreceptors within contracting skeletal muscles). In addition, the role of the cardiopulmonary baroreceptors in modulating the resetting of arterial baroreflex is identified, and the mechanisms in the central nervous system involved with the resetting of baroreflex function during dynamic exercise are also described. Approaching a very relevant clinical condition, the review also presents the concept that the impaired arterial baroreflex function is an integral component of the metaboreflex-mediated exaggerated sympathetic tone in subjects with heart failure. This increased sympathetic activity has a major role in causing the depressed ventricular function observed during submaximal dynamic exercise in these patients. The potential contribution of a metaboreflex arising from respiratory muscles is also considered.
Keywords: autonomic; baroreflex; central command; exercise; metaboreflex.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Ansorge EJ, Augustyniak RA, Perinot ML, Hammond RL, Kim JK, Sala-Mercado JA, Rodriguez J, Rossi NF, O'Leary DS. Altered muscle metaboreflex control of coronary blood flow and ventricular function in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288: H1381–H1388, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Augustyniak RA, Collins HL, Ansorge EJ, Rossi NF, O'Leary DS. Severe exercise alters the strength and mechanisms of the muscle metaboreflex. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H1645–H1652, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa TC, Fernandes IA, Magalhães-Jr N, Cavalcanti IL, Secher NH, Nóbrega AC, Vianna LC. Oscillatory blood pressure response to the onset of cycling exercise in men: role of group III/IV muscle afferents. Exp Physiol 100: 302–311, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

