Oxidative and nitrative stress in neurodegeneration
- PMID: 26024962
- PMCID: PMC4662638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.04.020
Oxidative and nitrative stress in neurodegeneration
Abstract
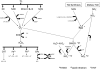
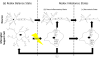
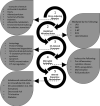
Aerobes require oxygen for metabolism and normal free radical formation. As a result, maintaining the redox homeostasis is essential for brain cell survival due to their high metabolic energy requirement to sustain electrochemical gradients, neurotransmitter release, and membrane lipid stability. Further, brain antioxidant levels are limited compared to other organs and less able to compensate for reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) generation which contribute oxidative/nitrative stress (OS/NS). Antioxidant treatments such as vitamin E, minocycline, and resveratrol mediate neuroprotection by prolonging the incidence of or reversing OS and NS conditions. Redox imbalance occurs when the antioxidant capacity is overwhelmed, consequently leading to activation of alternate pathways that remain quiescent under normal conditions. If OS/NS fails to lead to adaptation, tissue damage and injury ensue, resulting in cell death and/or disease. The progression of OS/NS-mediated neurodegeneration along with contributions from microglial activation, dopamine metabolism, and diabetes comprise a detailed interconnected pathway. This review proposes a significant role for OS/NS and more specifically, lipid peroxidation (LPO) and other lipid modifications, by triggering microglial activation to elicit a neuroinflammatory state potentiated by diabetes or abnormal dopamine metabolism. Subsequently, sustained stress in the neuroinflammatory state overwhelms cellular defenses and prompts neurotoxicity resulting in the onset or amplification of brain damage.
Keywords: Brain; Dopamine metabolism; Lipid peroxidation; Lipid/protein modification; Microglial activation; Neurodegeneration; Nitrative stress; Oxidative stress; Reactive nitrogen species; Reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ali TK, Matragoon S, Pillai BA, Liou GI, El-Remessy AB. Peroxynitrite mediates retinal neurodegeneration by inhibiting nerve growth factor survival signaling in experimental and human diabetes. Diabetes. 2008;57:889–898. - PubMed
-
- Ara J, Przedborski S, Naini AB, Jackson-Lewis V, Trifiletti RR, Horwitz J, Ischiropoulos H. Inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nitration following exposure to peroxynitrite and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95:7659–7663. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bajo-Graneras R, Ganfornina MD, Martin-Tejedor E, Sanchez D. Apolipoprotein D mediates autocrine protection of astrocytes and controls their reactivity level, contributing to the functional maintenance of paraquat-challenged dopaminergic systems. Glia. 2011;59:1551–1566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

