Novel contraceptive targets to inhibit ovulation: the prostaglandin E2 pathway
- PMID: 26025453
- PMCID: PMC4626744
- DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmv026
Novel contraceptive targets to inhibit ovulation: the prostaglandin E2 pathway
Abstract
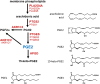
Background: Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an essential intrafollicular regulator of ovulation. In contrast with the one-gene, one-protein concept for synthesis of peptide signaling molecules, production and metabolism of bioactive PGE2 requires controlled expression of many proteins, correct subcellular localization of enzymes, coordinated PGE2 synthesis and metabolism, and prostaglandin transport in and out of cells to facilitate PGE2 action and degradation. Elevated intrafollicular PGE2 is required for successful ovulation, so disruption of PGE2 synthesis, metabolism or transport may yield effective contraceptive strategies.
Methods: This review summarizes case reports and studies on ovulation inhibition in women and macaques treated with cyclooxygenase inhibitors published from 1987 to 2014. These findings are discussed in the context of studies describing levels of mRNA, protein, and activity of prostaglandin synthesis and metabolic enzymes as well as prostaglandin transporters in ovarian cells.
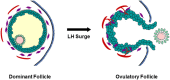
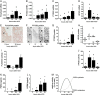
Results: The ovulatory surge of LH regulates the expression of each component of the PGE2 synthesis-metabolism-transport pathway within the ovulatory follicle. Data from primary ovarian cells and cancer cell lines suggest that enzymes and transporters can cooperate to optimize bioactive PGE2 levels. Elevated intrafollicular PGE2 mediates key ovulatory events including cumulus expansion, follicle rupture and oocyte release. Inhibitors of the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) enzyme (also known as cyclooxygenase-2 or COX2) reduce ovulation rates in women. Studies in macaques show that PTGS2 inhibitors can reduce the rates of cumulus expansion, oocyte release, follicle rupture, oocyte nuclear maturation and fertilization. A PTGS2 inhibitor reduced pregnancy rates in breeding macaques when administered to simulate emergency contraception. However, PTGS2 inhibition did not prevent pregnancy in monkeys when administered to simulate monthly contraceptive use.
Conclusion: PTGS2 inhibitors alone may be suitable for use as emergency contraceptives. However, drugs of this class are unlikely to be effective as monthly contraceptives. Inhibitors of additional PGE2 synthesis enzymes or modulation of PGE2 metabolism or transport also hold potential for reducing follicular PGE2 and preventing ovulation. Approaches which target multiple components of the PGE2 synthesis-metabolism-transport pathway may be required to effectively block ovulation and lead to the development of novel contraceptive options for women. Therapies which target PGE2 may also impact disorders of the uterus and could also have benefits for women's health in addition to contraception.
Keywords: contraception; follicle; ovary; prostaglandin E2, cyclooxygenase-2.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Akil M, Amos RS, Stewart P. Infertility may sometimes be associated with NSAID consumption. Br J Rheumatol 1996;35:76–78. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DT, Grinwich DL. Blockade of spontaneous and LH-induced ovulation in rats by indomethacin, an inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis. Prostaglandins 1972;1:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Athanasiou S, Bourne TH, Khalid A, Okokon EV, Crayford TJ, Hagstrom HG, Campbell S, Collins WP. Effects of indomethacin on follicular structure, vascularity, and function over the periovulatory period in women. Fertil Steril 1996;65:556–560. - PubMed
-
- Baillargeon JP, McClish DK, Essah PA, Nestler JE. Association between the current use of low-dose oral contraceptives and cardiovascular arterial disease: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:3863–3870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

