Hybrid Graphene Oxide Based Plasmonic-Magnetic Multifunctional Nanoplatform for Selective Separation and Label-Free Identification of Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers
- PMID: 26027901
- PMCID: PMC4677996
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b03619
Hybrid Graphene Oxide Based Plasmonic-Magnetic Multifunctional Nanoplatform for Selective Separation and Label-Free Identification of Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers
Abstract
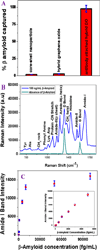
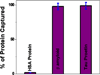
Despite intense efforts, Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the top public health crisis for society even at 21st century. Since presently there is no cure for AD, early diagnosis of possible AD biomarkers is crucial for the society. Driven by the need, the current manuscript reports the development of magnetic core-plasmonic shell nanoparticle attached hybrid graphene oxide based multifunctional nanoplatform which has the capability for highly selective separation of AD biomarkers from whole blood sample, followed by label-free surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) identification in femto gram level. Experimental ELISA data show that antibody-conjugated nanoplatform has the capability to capture more than 98% AD biomarkers from the whole blood sample. Reported result shows that nanoplatform can be used for SERS "fingerprint" identification of β-amyloid and tau protein after magnetic separation even at 100 fg/mL level. Experimental results indicate that very high sensitivity achieved is mainly due to the strong plasmon-coupling which generates huge amplified electromagnetic fields at the "hot spot". Experimental results with nontargeted HSA protein, which is one of the most abundant protein components in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), show that multifunctional nanoplatform based AD biomarkers separation and identification is highly selective.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers; fingerprint identification of β-amyloid and tau protein; hybrid graphene oxide; plasmonic-magnetic multifunctional nanoplatform; surface enhance Raman spectrosocpy.
Figures


References
-
- Dementia: A Public Health Priority. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2015 Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. http://www.alz.org/facts/overview.asp#mortality.
-
- Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi MH. The Global Burden Of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia. 2007;3:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann T, Bieger SC, Brühl B, Tienari PJ, Ida N, Allsop D, Roberts GW, Masters CL, Dotti CG, Unsicker K, Beyreuther K. Distinct Sites Of Intracellular Production For Alzheimer’s Disease Aβ40/42 Amyloid Peptides. Nat. Med. 1997;3:1016–1020. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, Hampel H, Weiner M, Zetterberg H. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Biomarkers in Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010;6:131–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

