HIF1α Represses Cell Stress Pathways to Allow Proliferation of Hypoxic Fetal Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 26028220
- PMCID: PMC4509618
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.04.021
HIF1α Represses Cell Stress Pathways to Allow Proliferation of Hypoxic Fetal Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
Transcriptional mediators of cell stress pathways, including HIF1α, ATF4, and p53, are key to normal development and play critical roles in disease, including ischemia and cancer. Despite their importance, mechanisms by which pathways mediated by these transcription factors interact with one another are not fully understood. In addressing the controversial role of HIF1α in cardiomyocytes (CMs) during heart development, we discovered a mid-gestational requirement for HIF1α for proliferation of hypoxic CMs, involving metabolic switching and a complex interplay among HIF1α, ATF4, and p53. Loss of HIF1α resulted in activation of ATF4 and p53, the latter inhibiting CM proliferation. Bioinformatic and biochemical analyses revealed unexpected mechanisms by which HIF1α intersects with ATF4 and p53 pathways. Our results highlight previously undescribed roles of HIF1α and interactions among major cell stress pathways that could be targeted to enhance proliferation of CMs in ischemia and may have relevance to other diseases, including cancer.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

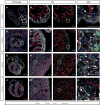

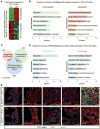

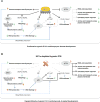
References
-
- Denko NC. Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:705–713. - PubMed
-
- Dunwoodie SL. The Role of Hypoxia in Development of the Mammalian Embryo. Dev Cell. 2009;17:755–773. - PubMed
-
- Fels DR, Koumenis C. The PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth. Cancer Bio & Ther. 2006;5:723–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- GM068524/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL106968/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL119967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK092062/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL117649/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL098053-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD006428/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL106968/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK094729/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094729/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092062/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066276/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 HL117649/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL098053/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL66100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

