Prmt5 is a regulator of muscle stem cell expansion in adult mice
- PMID: 26028225
- PMCID: PMC4458870
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8140
Prmt5 is a regulator of muscle stem cell expansion in adult mice
Abstract
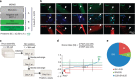
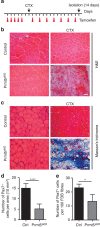
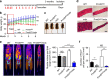
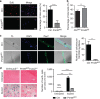
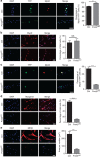
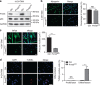
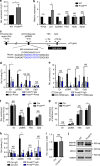
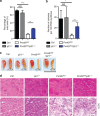
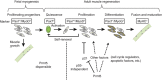
Skeletal muscle stem cells (MuSC), also called satellite cells, are indispensable for maintenance and regeneration of adult skeletal muscles. Yet, a comprehensive picture of the regulatory events controlling the fate of MuSC is missing. Here, we determine the proteome of MuSC to design a loss-of-function screen, and identify 120 genes important for MuSC function including the arginine methyltransferase Prmt5. MuSC-specific inactivation of Prmt5 in adult mice prevents expansion of MuSC, abolishes long-term MuSC maintenance and abrogates skeletal muscle regeneration. Interestingly, Prmt5 is dispensable for proliferation and differentiation of Pax7(+) myogenic progenitor cells during mouse embryonic development, indicating significant differences between embryonic and adult myogenesis. Mechanistic studies reveal that Prmt5 controls proliferation of adult MuSC by direct epigenetic silencing of the cell cycle inhibitor p21. We reason that Prmt5 generates a poised state that keeps MuSC in a standby mode, thus allowing rapid MuSC amplification under disease conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson A. et al. Hematopoietic stem cells reversibly switch from dormancy to self-renewal during homeostasis and repair. Cell 135, 1118–1129 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Seale P. et al. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell 102, 777–786 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Relaix F., Rocancourt D., Mansouri A. & Buckingham M. A Pax3/Pax7-dependent population of skeletal muscle progenitor cells. Nature 435, 948–953 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

