Transactivation Function-2 of Estrogen Receptor α Contains Transactivation Function-1-regulating Element
- PMID: 26028650
- PMCID: PMC4498094
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.638650
Transactivation Function-2 of Estrogen Receptor α Contains Transactivation Function-1-regulating Element
Abstract
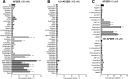
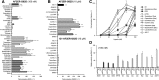
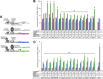
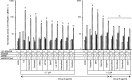
ERα has a ligand-dependent transactivation function in the ligand binding domain of ERα C terminus (AF-2) and a ligand-independent activation function in the N terminus (AF-1). It is still not fully understood how AF-1 and AF-2 activities are regulated cooperatively by ligands. To evaluate the AF-1 involvement in the estrogenic activities of various compounds, we analyzed these transactivation functions using AF-1-truncated and AF-2-mutated ERα mutants. AF-2 is composed of two domains with flexible and static regions. We used an AF-2 flexible region mutant and an AF-2 static region mutant. Both mutants have been reported as non-E2 responsive due to disruption of E2-mediated coactivator recruitment to the AF-2. The AF-2 mutants were not activated by agonists, but surprisingly antagonists and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) activated the AF-2 mutants. This antagonist reversal activity was derived from AF-1. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the AF-2 contains an AF-1 suppression function using C-terminal-truncated ERα mutants. From these findings we hypothesized that the mutation of AF-2 disrupted its ability to suppress AF-1, causing the antagonist reversal. To assess the AF-2-mediated AF-1 suppression, we analyzed the transcription activity of physically separated AF-1 and AF-2 using a novel hybrid reporter assay. We observed that the AF-1 activity was not suppressed by the physically separated AF-2. Furthermore, SERMs did not induce the AF-1-mediated activity from the separated mutant AF-2, which differed from the intact protein. These results imply that SERM activity is dependent on a conformational change of the full-length ERα molecule, which allows for AF-1 activation.
Keywords: agonist; antagonist; estrogen; estrogen receptor; protein structure; selected estrogen receptor modulators; steroid hormone; steroid hormone receptor.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures








References
-
- Couse J. F., Korach K. S. (1999) Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr. Rev. 20, 358–417 - PubMed
-
- Nettles K. W., Greene G. L. (2005) Ligand control of coregulator recruitment to nuclear receptors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 67, 309–333 - PubMed
-
- Blair R. M., Fang H., Branham W. S. (2000) The estrogen receptor relative binding affinities of 188 natural and xenochemicals: structural diversity of ligands. Toxicol. Sci. 54, 138–153 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

