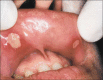
Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis for dental practitioners
- PMID: 26028911
- PMCID: PMC4441245
Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis for dental practitioners
Abstract
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) is a well-known oral disease with unclear etiopathogenesis for which symptomatic therapy is only available. This kind of study aimed to highlight the main points that the general practitioners should be taken in their consideration. We have collected our data from PubMed line from 1972 to 2011. Our criteria included the papers that refer to the general predisposing factors, and the general treatment of RAS. Some papers which indicated to the specific details related to RAS that needed a consultant or specialist in Oral Medicine have not included. There is no clear guideline of the etiology, diagnosis, and management of RAS; therefore, the majority of the general practitioners refer most of the cases to appropriate specialist.
Keywords: Aphthous stomatitis; etiological factors; major aphthous stomatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Barrons RW. Treatment strategies for recurrent oral aphthous ulcers. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2001;58(1):41–50. - PubMed
-
- Stanley HR. Aphthous lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972;33(3):40716. - PubMed
-
- Rogers RS., 3rd Recurrent aphthous stomatitis: Clinical characteristics and associated systemic disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1997;16(4):278–83. - PubMed
-
- Scully C, Porter S. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis: Current concepts of etiology, pathogenesis and management. J Oral Pathol Med. 1989;18(1):21–7. - PubMed
-
- Sircus W, Church R, Kelleher J. Recurrent aphthous ulceration of the mouth;a study of the natural history, aetiology, and treatment. Q J Med. 1957;26(102):235–49. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical