Severe respiratory failure due to co-infection with human metapneumovirus and Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 26029528
- PMCID: PMC4061431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2013.12.007
Severe respiratory failure due to co-infection with human metapneumovirus and Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
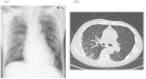
A 64-year-old male patient was admitted with respiratory failure, although chest X-rays revealed only mild bronchiolitis. Streptococcus pneumoniae, which usually presents as massive lobular pneumonia, was isolated from sputum, however, pan-pathogen screening using a next-generation sequencer also detected human metapneumovirus genome fragments.
Keywords: Co-infection; Human metapneumovirus; Next-generation sequencer; Real-time PCR; Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Figures

References
-
- Boivin G., Abed Y., Pelletier G., Ruel L., Moisan D., Côté S. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with human metapneumovirus: a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory-tract infections in all age groups. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1330–1340. - PubMed
-
- Deyde V.M., Xu X., Bright R.A., Shaw M., Smith C.B., Zhang Y. Surveillance of resistance to adamantanes among influenza A(H3N2) and A(H1N1) viruses isolated worldwide. Infect Dis. 2007;196:630–632. - PubMed
-
- Boivin G., De Serres G., Hamelin M.E., Côté S., Argouin M., Tremblay G. An outbreak of severe respiratory tract infection due to human metapneumovirus in a long-term care facility. 2007;44:1152–1158. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

