Accelerated wound healing by injectable microporous gel scaffolds assembled from annealed building blocks
- PMID: 26030305
- PMCID: PMC4615579
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat4294
Accelerated wound healing by injectable microporous gel scaffolds assembled from annealed building blocks
Abstract
Injectable hydrogels can provide a scaffold for in situ tissue regrowth and regeneration, yet gel degradation before tissue reformation limits the gels' ability to provide physical support. Here, we show that this shortcoming can be circumvented through an injectable, interconnected microporous gel scaffold assembled from annealed microgel building blocks whose chemical and physical properties can be tailored by microfluidic fabrication. In vitro, cells incorporated during scaffold formation proliferated and formed extensive three-dimensional networks within 48 h. In vivo, the scaffolds facilitated cell migration that resulted in rapid cutaneous-tissue regeneration and tissue-structure formation within five days. The combination of microporosity and injectability of these annealed gel scaffolds should enable novel routes to tissue regeneration and formation in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no competing financial interests.
Figures

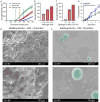
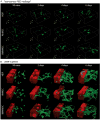
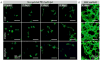
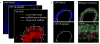

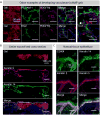
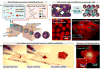
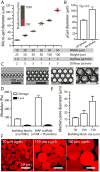




Comment in
-
Wound healing: Enzymatically crosslinked scaffolds.Nat Mater. 2015 Jul;14(7):662-3. doi: 10.1038/nmat4337. Nat Mater. 2015. PMID: 26099714 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee K, Hubbell JA. Tissue, cell and engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24:827–829. - PubMed
-
- Wade RJ, Burdick JA. Engineering ECM signals into biomaterials. Mater Today. 2012;15:454–459.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

