Serum HE4: An Independent Prognostic Factor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26030627
- PMCID: PMC4452338
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128836
Serum HE4: An Independent Prognostic Factor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
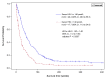
Human epididymis secretory protein 4 (HE4) is a secreted glycosylated protein encoded by the WAP four-disulfide core domain 2 (WFDC2) gene, located on a chromosome 20 segment that is frequently amplified in many cancers. This study aimed at determining serum HE4 prognostic value in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), following the REMARK guidelines. Serum samples from 346 consecutive patients with histologically proven and previously untreated NSCLC and 41 patients with benign pulmonary disease were collected at the Montpellier-Nimes Academic Hospital. Work-up investigations performed to determine the disease characteristics and treatment algorithms were congruent with international guidelines. HE4 levels in serum were measured with an ELISA test (Fujirebio Diagnostics) that uses two monoclonal antibodies, 2H5 and 3D8, against the C-WFDC domain of HE4. The area under the ROC curve (i.e., overall ability of HE4 to discriminate between controls and patients) was 0.78 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.738-0.821; z test P <0.0001). Serum HE4 levels were significantly higher in patients with worse performance status, advanced TNM stage and positive nodal status. In the Cox model, overall survival was shorter in patients with high pretreatment serum HE4 (above 140 pmol/L) than in patients with serum H4 level ≤ 140 pmol/L [median survival: 17.7 weeks (95% CI, 11.9 to 24.9) and 46.4 weeks (95% CI, 38.6 to 56.3), respectively; hazard ratio: 1.48 (95% CI, 1.12 to 1.95) for high HE4; adjusted P = 0.0057]. High serum HE4 level at diagnosis is an independent determinant of poor prognosis in NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Paesmans M, Sculier JP, Libert P, Bureau G, Dabouis G, Thiriaux J, et al. Response to chemotherapy has predictive value for further survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: 10 years experience of the European Lung Cancer Working Party. Eur J Cancer. 1997;33: 2326–32. - PubMed
-
- Charloux A, Hedelin G, Dietemann A, Ifoundza T, Roeslin N, Pauli G, et al. Prognostic value of histology in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 1997;17: 123–34. - PubMed
-
- Merrill RM, Henson DE, Barnes M. Conditional survival among patients with carcinoma of the lung. Chest. 1999;116: 697–703. - PubMed
-
- Komaki R, Pajak TF, Byhardt RW, Emami B, Asbell SO, Roach M 3rd, et al. Analysis of early and late deaths on RTOG non-small cell carcinoma of the lung trials: comparison with CALGB 8433. Lung Cancer. 1993;10: 189–97. - PubMed
-
- Furuse K, Fukuoka M, Kawahara M, Nishikawa H, Takada Y, Kudoh S, et al. Phase III study of concurrent versus sequential thoracic radiotherapy in combination with mitomycin, vindesine, and cisplatin in unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17: 2692–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

