The effects of whole body vibration on mobility and balance in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review with meta-analysis
- PMID: 26032205
- PMCID: PMC5133716
The effects of whole body vibration on mobility and balance in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review with meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of whole-body vibration on physiologic and functional measurements in children with cerebral palsy.
Design and methods: We searched MEDLINE, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, EMBASE, Scielo, CINAHL (from the earliest date available to November 2014) for randomized controlled trials, that aimed to investigate the effects of whole-body vibration versus exercise and/or versus control on physiologic and functional measurements in children with cerebral palsy. Two reviewers independently selected the studies. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
Results: Six studies with 176 patients comparing whole-body vibration to exercise and/or control were included. Whole-body vibration resulted in improvement in: gait speed WMDs (0.13 95% CI: 0.05 to 0.20); gross motor function dimension E WMDs (2.97 95% CI: 0.07 to 5.86) and femur bone density (1.32 95% CI: 0.28 to 2.36). The meta-analysis also showed a nonsignificant difference in muscle strength and gross motor function dimension D for participants in the whole-body vibration compared with control group. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: Whole-body vibration may improve gait speed and standing function in children with cerebral palsy and could be considered for inclusion in rehabilitation programs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures


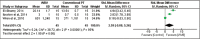


References
-
- Richards CL, Malouin F. Cerebral palsy: definition, assessment and rehabilitation. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;111:183–95. - PubMed
-
- Franki I, Desloovere K, De Cat J, Feys H, Molenaers G, Calders P. The evidence-base for basic physical therapy techniques targeting lower limb function in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health as a conceptual framework. J Rehabil Med. 2012;44:385–95. - PubMed
-
- Dickin DC, Faust KA, Wang H, Frame J. The acute effects of whole-body vibration on gait parameters in adults with cerebral palsy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2013;13:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Ahlborg L, Andersson C, Julin P. Whole-body vibration training compared with resistance training: effect on spasticity, muscle strength and motor performance in adults with cerebral palsy. J Rehabil Med. 2006;38(5):302–8. - PubMed
