Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2028 individuals with schizophrenia and 2540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium
- PMID: 26033243
- PMCID: PMC4668237
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2015.63
Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2028 individuals with schizophrenia and 2540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium
Erratum in
-
Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2028 individuals with schizophrenia and 2540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium.Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr;21(4):585. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.118. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26283641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
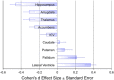
The profile of brain structural abnormalities in schizophrenia is still not fully understood, despite decades of research using brain scans. To validate a prospective meta-analysis approach to analyzing multicenter neuroimaging data, we analyzed brain MRI scans from 2028 schizophrenia patients and 2540 healthy controls, assessed with standardized methods at 15 centers worldwide. We identified subcortical brain volumes that differentiated patients from controls, and ranked them according to their effect sizes. Compared with healthy controls, patients with schizophrenia had smaller hippocampus (Cohen's d=-0.46), amygdala (d=-0.31), thalamus (d=-0.31), accumbens (d=-0.25) and intracranial volumes (d=-0.12), as well as larger pallidum (d=0.21) and lateral ventricle volumes (d=0.37). Putamen and pallidum volume augmentations were positively associated with duration of illness and hippocampal deficits scaled with the proportion of unmedicated patients. Worldwide cooperative analyses of brain imaging data support a profile of subcortical abnormalities in schizophrenia, which is consistent with that based on traditional meta-analytic approaches. This first ENIGMA Schizophrenia Working Group study validates that collaborative data analyses can readily be used across brain phenotypes and disorders and encourages analysis and data sharing efforts to further our understanding of severe mental illness.
Figures
References
-
- Ward KE, Friedman L, Wise A, Schulz SC. Meta-analysis of brain and cranial size in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1996; 22: 197–213. - PubMed
-
- Nelson MD, Saykin AJ, Flashman LA, Riordan HJ. Hippocampal volume reduction in schizophrenia as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging: a meta-analytic study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998; 55: 433–440. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 104036/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 EB006841/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000153/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB020407/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH097435/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103472/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB005846/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094524/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH085096/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

