Emerging roles of sumoylation in the regulation of actin, microtubules, intermediate filaments, and septins
- PMID: 26033929
- PMCID: PMC5049490
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21226
Emerging roles of sumoylation in the regulation of actin, microtubules, intermediate filaments, and septins
Abstract
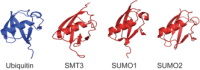
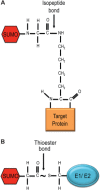
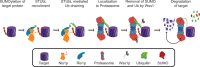
Sumoylation is a powerful regulatory system that controls many of the critical processes in the cell, including DNA repair, transcriptional regulation, nuclear transport, and DNA replication. Recently, new functions for SUMO have begun to emerge. SUMO is covalently attached to components of each of the four major cytoskeletal networks, including microtubule-associated proteins, septins, and intermediate filaments, in addition to nuclear actin and actin-regulatory proteins. However, knowledge of the mechanisms by which this signal transduction system controls the cytoskeleton is still in its infancy. One story that is beginning to unfold is that SUMO may regulate the microtubule motor protein dynein by modification of its adaptor Lis1. In other instances, cytoskeletal elements can both bind to SUMO non-covalently and also be conjugated by it. The molecular mechanisms for many of these new functions are not yet clear, but are under active investigation. One emerging model links the function of MAP sumoylation to protein degradation through SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases, also known as STUbL enzymes. Other possible functions for cytoskeletal sumoylation are also discussed.
Keywords: IF; MAPs; MT; SUMO; microfilaments; microtubule-associated proteins; septins.
© 2015 The Authors. Cytoskeleton Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

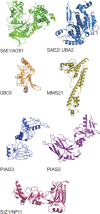
References
-
- Adhikari AS, Sridhar Rao K, Rangaraj N, Parnaik VK, Mohan Rao CH. 2004. Heat stress‐induced localization of small heat shock proteins in mouse myoblasts: intranuclear lamin A/C speckles as target for alphaB‐crystallin and Hsp25. Exp Cell Res 299:393–403. - PubMed
-
- Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L. 1986. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate‐type filaments. Nature 323:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. 2008. Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Akyurek N, Ren Y, Rassidakis GZ, Schlette EJ, Medeiros LJ. 2006. Expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in B‐cell non‐Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphomas. Cancer 107:1844–1851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

