Genetic absence of PD-1 promotes accumulation of terminally differentiated exhausted CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 26034050
- PMCID: PMC4493417
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20142237
Genetic absence of PD-1 promotes accumulation of terminally differentiated exhausted CD8+ T cells
Abstract
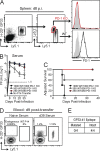
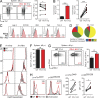
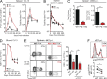
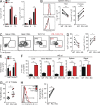
Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) has received considerable attention as a key regulator of CD8(+) T cell exhaustion during chronic infection and cancer because blockade of this pathway partially reverses T cell dysfunction. Although the PD-1 pathway is critical in regulating established "exhausted" CD8(+) T cells (TEX cells), it is unclear whether PD-1 directly causes T cell exhaustion. We show that PD-1 is not required for the induction of exhaustion in mice with chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection. In fact, some aspects of exhaustion are more severe with genetic deletion of PD-1 from the onset of infection. Increased proliferation between days 8 and 14 postinfection is associated with subsequent decreased CD8(+) T cell survival and disruption of a critical proliferative hierarchy necessary to maintain exhausted populations long term. Ultimately, the absence of PD-1 leads to the accumulation of more cytotoxic, but terminally differentiated, CD8(+) TEX cells. These results demonstrate that CD8(+) T cell exhaustion can occur in the absence of PD-1. They also highlight a novel role for PD-1 in preserving TEX cell populations from overstimulation, excessive proliferation, and terminal differentiation.
© 2015 Odorizzi et al.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI105343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI117718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI117718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI112521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI112521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN266200500030C/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 AI105343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN266200500030C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

