A large multiethnic genome-wide association study of prostate cancer identifies novel risk variants and substantial ethnic differences
- PMID: 26034056
- PMCID: PMC4527942
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0315
A large multiethnic genome-wide association study of prostate cancer identifies novel risk variants and substantial ethnic differences
Abstract
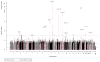
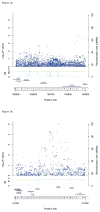
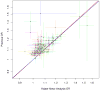
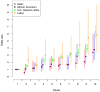
A genome-wide association study (GWAS) of prostate cancer in Kaiser Permanente health plan members (7,783 cases, 38,595 controls; 80.3% non-Hispanic white, 4.9% African-American, 7.0% East Asian, and 7.8% Latino) revealed a new independent risk indel rs4646284 at the previously identified locus 6q25.3 that replicated in PEGASUS (N = 7,539) and the Multiethnic Cohort (N = 4,679) with an overall P = 1.0 × 10(-19) (OR, 1.18). Across the 6q25.3 locus, rs4646284 exhibited the strongest association with expression of SLC22A1 (P = 1.3 × 10(-23)) and SLC22A3 (P = 3.2 × 10(-52)). At the known 19q13.33 locus, rs2659124 (P = 1.3 × 10(-13); OR, 1.18) nominally replicated in PEGASUS. A risk score of 105 known risk SNPs was strongly associated with prostate cancer (P < 1.0 × 10(-8)). Comparing the highest to lowest risk score deciles, the OR was 6.22 for non-Hispanic whites, 5.82 for Latinos, 3.77 for African-Americans, and 3.38 for East Asians. In non-Hispanic whites, the 105 risk SNPs explained approximately 7.6% of disease heritability. The entire GWAS array explained approximately 33.4% of heritability, with a 4.3-fold enrichment within DNaseI hypersensitivity sites (P = 0.004).
Significance: Taken together, our findings of independent risk variants, ethnic variation in existing SNP replication, and remaining unexplained heritability have important implications for further clarifying the genetic risk of prostate cancer. Our findings also suggest that there may be much promise in evaluating understudied variation, such as indels and ethnically diverse populations.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hayes RB, Liff JM, Pottern LM, Greenberg RS, Schoenberg JB, Schwartz AG, et al. Prostate cancer risk in U.S. blacks and whites with a family history of cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 1995;60:361–4. - PubMed
-
- Whittemore AS, Wu AH, Kolonel LN, John EM, Gallagher RP, Howe GR, et al. Family history and prostate cancer risk in black, white, and Asian men in the United States and Canada. Am J Epidemiol. 1995;141:732–40. - PubMed
-
- Schaid DJ. The complex genetic epidemiology of prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(Spec No 1):R103–21. - PubMed
-
- Baker SG, Lichtenstein P, Kaprio J, Holm N. Genetic susceptibility to prostate, breast, and colorectal cancer among Nordic twins. Biometrics. 2005;61:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB009383/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA127298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA136578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA112355/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1326792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA131945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM067547/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA088164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA112355/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA127298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA141298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157881/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA112355/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM107427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- AG046616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DC013300/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC013300/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA151254/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA157881/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG046616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States

