Comparative analysis of photograph-based clinical goniometry to standard techniques
- PMID: 26034439
- PMCID: PMC4447686
- DOI: 10.1007/s11552-014-9702-2
Comparative analysis of photograph-based clinical goniometry to standard techniques
Abstract
Background: Assessment of joint range of motion (ROM) is an accepted evaluation of disability as well as an indicator of recovery from musculoskeletal injuries. Many goniometric techniques have been described to measure ROM, with variable validity due to inter-rater reliability. In this report, we assessed the validity of photograph-based goniometry in measurement of ROM and its inter-rater reliability and compared it to two other commonly used techniques.
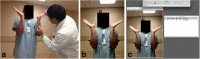
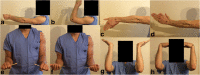
Methods: We examined three methods for measuring ROM in the upper extremity: manual goniometry (MG), visual estimations (VE), and photograph-based goniometry (PBG). Eight motions of the upper extremity were measured in 69 participants at an academic medical center.
Results: We found visual estimations and photograph-based goniometry to be clinically valid when tested against manual goniometry (r avg. 0.58, range 0.28 to 0.87). Photograph-based measurements afforded a satisfactory degree of inter-rater reliability (ICC avg. 0.77, range 0.28 to 0.96).
Conclusions: Our study supports photograph-based goniometry as the new standard goniometric technique, as it has been clinically validated, is performed with greater consistency and better inter-rater reliability when compared with manual goniometry. It also allows for better documentation of measurements and potential incorporation into medical records in direct contrast to visual estimation.
Keywords: Goniometry; Photograph; Range of motion; Visual estimation.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

