Influenza virus vaccination and kidney graft rejection: causality or coincidence
- PMID: 26034595
- PMCID: PMC4440474
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfv027
Influenza virus vaccination and kidney graft rejection: causality or coincidence
Abstract
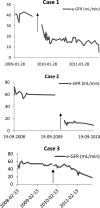
Influenza can cause significant morbidity and mortality in renal transplant recipients especially with a high rate of lower respiratory disease. Annual influenza vaccination is therefore recommended to renal transplant recipients. We report the first three cases of acute kidney injury in renal transplant recipients following influenza vaccination that all led to graft loss. They all had different native diseases and were all vaccinated in the same season of 2009-10. The time span from vaccination to decline of kidney function is shorter than the time to diagnosis since the three patients only had blood tests every 3 months or when symptoms became severe. These reports do not justify a change of current recommendations regarding influenza vaccination in renal transplant recipients, but they support the continued attention and registration of vaccinations to monitor side effects.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; influenza vaccination; kidney graft rejection; renal transplant recipient.
Figures
References
-
- Siegrist CA, Ambrosioni J, Bel M, et al. Responses of solid organ transplant recipients to the AS03-adjuvanted pandemic influenza vaccine. Antivir Ther 2012; 17: 893–903 - PubMed
-
- Kumar D, Blumberg EA, Danziger-Isakov L, et al. Influenza vaccination in the organ transplant recipient: review and summary recommendations. Am J Transplant 2011; 11: 2020–2030 - PubMed
-
- Raman KS, Chandrasekar T, Reeve RS, et al. Influenza vaccine-induced rhabdomyolysis leading to acute renal transplant dysfunction. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: 530–531 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources