A 1H-NMR-Based Metabonomic Study on the Anti-Depressive Effect of the Total Alkaloid of Corydalis Rhizoma
- PMID: 26035102
- PMCID: PMC6272534
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200610047
A 1H-NMR-Based Metabonomic Study on the Anti-Depressive Effect of the Total Alkaloid of Corydalis Rhizoma
Abstract
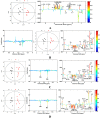
Corydalis Rhizoma, named YuanHu in China, is the dried tuber of Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang which is used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for pain relief and blood activation. Previous pharmacological studies showed that apart from analgesics, the alkaloids from YuanHu may be useful in the therapy of depression by acting on the GABA, dopamine and benzodiazepine receptors. In this study, the antidepressive effect of the total alkaloid of YuanHu (YHTA) was investigated in a chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) rat model using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Plasma metabolic profiles were analyzed and multivariate data analysis was applied to discover the metabolic biomarkers in CUMS rats. Thirteen biomarkers of CUMS-introduced depression were identified, which are myo-inositol, glycerol, glycine, creatine, glutamine, glutamate, β-glucose, α-glucose, acetoacetate, 3-hydroxybutyrate, leucine and unsaturated lipids (L7, L9). Moreover, a metabolic network of the potential biomarkers in plasma perturbed by CUMS was detected. After YHTA treatment, clear separation between the model group and YHTA-treated group was achieved. The levels of all the abnormal metabolites mentioned above showed a tendency of restoration to normal levels. The results demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of YHTA against depression and suggested that NMR-based metabolomics can provide a simple and easy tool for the evaluation of herbal therapeutics.
Keywords: 1H-NMR; OPLS-DA; corydalis rhizoma; depression; metabonomics; plasma; total alkaloids of YuanHu (YHTA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Charney D.S. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 1998;59:11–14. - PubMed
-
- Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2010. Volume 1. Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2010. Editorial Committee for the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; p. 133.
-
- Wang X.L., Zheng Z., Hong Z., Fan G. Advancements on chemical components and quality control of rhizoma corydalis. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2011;22:227–229.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

