CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 26035283
- PMCID: PMC4649911
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10833
CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus
Abstract
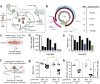
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is prevalent, deadly, and seldom cured due to the persistence of viral episomal DNA (cccDNA) in infected cells. Newly developed genome engineering tools may offer the ability to directly cleave viral DNA, thereby promoting viral clearance. Here, we show that the CRISPR/Cas9 system can specifically target and cleave conserved regions in the HBV genome, resulting in robust suppression of viral gene expression and replication. Upon sustained expression of Cas9 and appropriately chosen guide RNAs, we demonstrate cleavage of cccDNA by Cas9 and a dramatic reduction in both cccDNA and other parameters of viral gene expression and replication. Thus, we show that directly targeting viral episomal DNA is a novel therapeutic approach to control the virus and possibly cure patients.
Figures

References
-
- Ganem D. & Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem 56, 651–693 (1987). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110049/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08DK101754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5DP1-MH100706/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA14051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES002109/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 8 UL1 TR000043/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 MH100706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5R01-NS073124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK101754/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-ES002109/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

