Quality of Life in Patients with NSCLC Receiving Maintenance Therapy
- PMID: 26035509
- PMCID: PMC4491692
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers7020817
Quality of Life in Patients with NSCLC Receiving Maintenance Therapy
Abstract
Introduction: In the past few years many trials have evaluated the use of maintenance therapy in the treatment of NSCLC stage IV. Both switch as well as continuation maintenance show an improved PFS and overall survival. HRQoL data was only partially published. The aim of this article is to review the published effects of maintenance therapy on HRQoL.
Methods: Two PubMed searches were performed using the terms: "maintenance therapy and NSCLC" and "maintenance therapy and NSCLC and HRQoL". The published data was compared, analysed and evaluated.
Results: 272 articles were found dealing with maintenance therapy, and of these 85 articles were found regarding maintenance therapy and HRQoL in NSCLC. Maintenance therapy showed no negative impact on HRQoL but failed to show a real benefit. Some symptoms showed positive trends during maintenance therapy. HRQoL can be used to select patients for maintenance therapy.
Conclusions: Maintenance therapy is very safe, improves PFS and OS without impairing HRQoL. Although a positive impact on general QoL could not be demonstrated this is possibly due to the mode of evaluating HRQoL. Patient reported outcomes should be simplified and examined for a longer period of time.
Keywords: HRQoL; NSCLC; maintenance therapy.
Figures
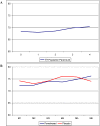
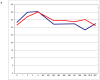

References
-
- Cappuzzo F., Ciuleanu T., Stelmakh L., Cicenas S., Szczésna A., Juhász E., Esteban E., Molinier O., Brugger W., Melezínek I., et al. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:521–529. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70112-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ciuleanu T., Brodowicz T., Zielinski C., Kim J.H., Krzakowski M., Laack E., Wu Y.L., Bover I., Begbie S., Tzekova V., et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2009;374:1432–1440. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61497-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barlesi F., Scherpereel A., Rittmeyer A., Pazzola A., Ferrer T.N., Kim J.H., Ahn M.J., Aerts J.G., Gorbunova V., Vikström A., et al. Randomized phase III trial of maintenance bevacizumab with or without pemetrexed after first-line induction with bevacizumab, cisplatin, and pemetrexed in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAPERL (MO22089) J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:3004–3011. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.3749. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

