The fatty acid amide hydrolase C385A variant affects brain binding of the positron emission tomography tracer [11C]CURB
- PMID: 26036940
- PMCID: PMC4527995
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.119
The fatty acid amide hydrolase C385A variant affects brain binding of the positron emission tomography tracer [11C]CURB
Abstract
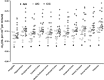
The common functional single-nucleotide polymorphism (rs324420, C385A) of the endocannabinoid inactivating enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) has been associated with anxiety disorder relevant phenotype and risk for addictions. Here, we tested whether the FAAH polymorphism affects in vivo binding of the FAAH positron emission tomography (PET) probe [(11)C]CURB ([(11)C-carbonyl]-6-hydroxy-[1,10-biphenyl]-3-yl cyclohexylcarbamate (URB694)). Participants (n=24) completed one [(11)C]CURB/PET scan and were genotyped for rs324420. Relative to C/C (58%), A-allele carriers (42%) had 23% lower [(11)C]CURB binding (λk3) in brain. We report evidence that the genetic variant rs324420 in FAAH is associated with measurable differences in brain FAAH binding as per PET [(11)C]CURB measurement.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez-Moreno JA, Echeverry-Alzate V, Buhler KM. The genetic basis of the endocannabinoid system and drug addiction in humans. J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Chiang KP, Gerber AL, Sipe JC, Cravatt BF. Reduced cellular expression and activity of the P129T mutant of human fatty acid amide hydrolase: evidence for a link between defects in the endocannabinoid system and problem drug use. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:2113–2119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical