Development of a Novel Urine Alzheimer-Associated Neuronal Thread Protein ELISA Kit and Its Potential Use in the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26037289
- PMCID: PMC6807133
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21856
Development of a Novel Urine Alzheimer-Associated Neuronal Thread Protein ELISA Kit and Its Potential Use in the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-related chronic degenerative disease that damages the nervous system. A noninvasive and simple method for early detection of AD is extremely important for the diagnosis and prognosis of AD. Thus, we aimed to develop an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit to detect urine Alzheimer-associated neuronal thread protein (AD7C-NTP), and to evaluate its clinical value for the diagnosis of AD.
Methods: Immunogenic AD7C-NTP peptide fragments were synthesized by the solid-phase method and used for immunizing mice or rabbits to generate anti-AD7C-NTP antibodies. The urine AD7C-NTP ELISA kit was then established; the generated mouse anti-AD7C-NTP antibody was used as a capture antibody, the biotin-labeled rabbit anti-AD7C-NTP antibody was used as a detection antibody, and avidin labeled by horseradish peroxidase was used as a substrate. The first morning urine specimens of 121 AD patients and 118 age-matched controls were collected, and the urine AD7C-NTP levels were detected by the above ELISA kit.
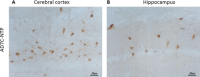
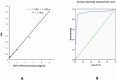
Results: Mouse and rabbit anti-AD7C-NTP antibody ELISA titer was found to be 1:8,000 and 1:32,000, respectively. A single band with a relative molecular mass of 41 kDa was found in human brain specimens by Western blot assay, which was identified as AD7C-NTP antibody. The urine AD7C-NTP concentration of the AD patients was higher than that of the age-matched controls, the sensitivity was 89.3% and the specificity was 84.7%.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that our newly developed urine AD7C-NTP ELISA kit has suggested potential for diagnosing AD in a Chinese population, suggesting it may be a useful diagnostic kit for detecting early AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Alzheimer-associated neuronal thread protein; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; urine.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no ethical/legal conflicts involved in the article.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

