An assessment of antibacterial activity of three pulp capping materials on Enterococcus faecalis by a direct contact test: An in vitro study
- PMID: 26038657
- PMCID: PMC4439853
- DOI: 10.4103/1305-7456.156837
An assessment of antibacterial activity of three pulp capping materials on Enterococcus faecalis by a direct contact test: An in vitro study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate antimicrobial activities of three different pulp capping materials; Biodentine, mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) Angelus, and Dycal against Enterococcus faecalis and their durability with time.
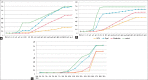
Materials and methods: Direct contact test was used for the assessment. Three sets of sealers were mixed and placed on microtiter plate wells: One set was used within 20 min of recommended setting time while others were used after 24-h and 1-week. E. faecalis suspension was placed directly on the materials for 1 h and then transferred to another plate with fresh media. Nine wells of bacteria without the tested cements served as the positive control. One well of the tested cements without bacteria served as the negative control. Bacterial growth was evaluated by a temperature-controlled microplate spectrophotometer for 1-h intervals among 24 h. Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results: All tested materials showed less bacterial density than the control group. MTA, Biodentine, and Dycal showed significantly higher bacterial density than the control group in freshly mixed samples (P < 0.05). And MTA showed significantly higher antibacterial activity than Dycal (P < 0.05). In 24 h, materials did not show any differences (P > 0.05). MTA and Biodentine samples showed significant differences than Dycal; MTA also showed higher antibacterial activity than control in 1-week samples (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: While freshly mixed MTA showed the best antibacterial activity over time, Biodentine had shown similar antibacterial activity to MTA.
Keywords: Antibacterial effect; Biodentine; Enterococcus faecalis; bacteria; calcium hydroxide; calcium silicate; dental materials; direct contact test; mineral trioxide aggregate; pulp capping.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mohammadi Z, Dummer PM. Properties and applications of calcium hydroxide in endodontics and dental traumatology. Int Endod J. 2011;44:697–730. - PubMed
-
- Schuurs AH, Gruythuysen RJ, Wesselink PR. Pulp capping with adhesive resin-based composite vs. calcium hydroxide: A review. Endod Dent Traumatol. 2000;16:240–50. - PubMed
-
- Farhad A, Mohammadi Z. Calcium hydroxide: A review. Int Dent J. 2005;55:293–301. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources