The approved pediatric drug suramin identified as a clinical candidate for the treatment of EV71 infection-suramin inhibits EV71 infection in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 26038755
- PMCID: PMC4185360
- DOI: 10.1038/emi.2014.60
The approved pediatric drug suramin identified as a clinical candidate for the treatment of EV71 infection-suramin inhibits EV71 infection in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
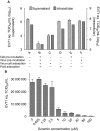
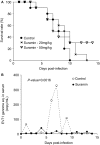
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) causes severe central nervous system infections, leading to cardiopulmonary complications and death in young children. There is an urgent unmet medical need for new pharmaceutical agents to control EV71 infections. Using a multidisciplinary approach, we found that the approved pediatric antiparasitic drug suramin blocked EV71 infectivity by a novel mechanism of action that involves binding of the naphtalentrisulonic acid group of suramin to the viral capsid. Moreover, we demonstrate that when suramin is used in vivo at doses equivalent to or lower than the highest dose already used in humans, it significantly decreased mortality in mice challenged with a lethal dose of EV71 and peak viral load in adult rhesus monkeys. Thus, suramin inhibits EV71 infection by neutralizing virus particles prior to cell attachment. Consequently, these findings identify suramin as a clinical candidate for further development as a therapeutic or prophylactic treatment for severe EV71 infection.
Keywords: anti-viral; drug discovery; enterovirus 71; hand, foot and mouth disease; suramin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suramin inhibits EV71 infection.Antiviral Res. 2014 Mar;103:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24374150
-
Protective effect of enterovirus‑71 (EV71) virus‑like particle vaccine against lethal EV71 infection in a neonatal mouse model.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):2473-80. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3680. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25936344 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structures of Yeast-Produced Enterovirus 71 and Enterovirus 71/Coxsackievirus A16 Chimeric Virus-Like Particles Provide the Structural Basis for Novel Vaccine Design against Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(12):6196-208. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00422-15. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25833050 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral drug discovery for the treatment of enterovirus 71 infections.Antiviral Res. 2013 Feb;97(2):183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.12.005. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23261847 Review.
-
Diseases caused by enterovirus 71 infection.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Oct;28(10):904-10. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181a41d63. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 20118685 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase by suramin.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Mar;28(3):319-325. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00570-0. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33674802
-
Understanding Enterovirus 71 Neuropathogenesis and Its Impact on Other Neurotropic Enteroviruses.Brain Pathol. 2015 Sep;25(5):614-24. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12279. Brain Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26276025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suramin interacts with the positively charged region surrounding the 5-fold axis of the EV-A71 capsid and inhibits multiple enterovirus A.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 20;7:42902. doi: 10.1038/srep42902. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28218309 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of Combinations of Enterovirus Inhibitors against Enterovirus 71.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5357-67. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01073-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27353263 Free PMC article.
-
100 Years of Suramin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Feb 21;64(3):e01168-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01168-19. Print 2020 Feb 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31844000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solomon T, Lewthwaite P, Perera D, Cardosa MJ, McMinn P, Ooi MH. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10:778–790. - PubMed
-
- Wang SM, Liu CC. Enterovirus 71: epidemiology, pathogenesis and management. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;7:735–742. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) WHO: Manila; 2013. Available at http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/HFMD/en/.
-
- Mirand A, Schuffenecker I, Henquell C, et al. Phylogenetic evidence for a recent spread of two populations of human enterovirus 71 in European countries. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:2263–2277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
