Large-scale serum protein biomarker discovery in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 26039989
- PMCID: PMC4466703
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1507719112
Large-scale serum protein biomarker discovery in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
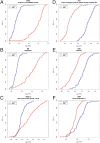
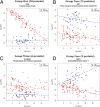
Serum biomarkers in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) may provide deeper insights into disease pathogenesis, suggest new therapeutic approaches, serve as acute read-outs of drug effects, and be useful as surrogate outcome measures to predict later clinical benefit. In this study a large-scale biomarker discovery was performed on serum samples from patients with DMD and age-matched healthy volunteers using a modified aptamer-based proteomics technology. Levels of 1,125 proteins were quantified in serum samples from two independent DMD cohorts: cohort 1 (The Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy-Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center), 42 patients with DMD and 28 age-matched normal volunteers; and cohort 2 (The Cooperative International Neuromuscular Research Group, Duchenne Natural History Study), 51 patients with DMD and 17 age-matched normal volunteers. Forty-four proteins showed significant differences that were consistent in both cohorts when comparing DMD patients and healthy volunteers at a 1% false-discovery rate, a large number of significant protein changes for such a small study. These biomarkers can be classified by known cellular processes and by age-dependent changes in protein concentration. Our findings demonstrate both the utility of this unbiased biomarker discovery approach and suggest potential new diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for ameliorating the burden of DMD and, we hope, other rare and devastating diseases.
Keywords: SOMAmer; SOMAscan; biomarkers; muscular dystrophy; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: L.G. is the founder and a stakeholder in SomaLogic, Inc; E.B., R.K.D., B.M., M.N., B.S., F.S., D.S., and S.W. are employees and stakeholders in SomaLogic, Inc.; Y.M.K. has been affiliated with the Eli Lilly and Co. since October 2012.
Figures
References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Ferlini A, Vroom E. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints in Duchenne: Meeting report. Neuromuscul Disord. 2014;24(8):743–745. - PubMed
-
- Bushby K, et al. DMD Care Considerations Working Group Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: Diagnosis, and pharmacological and psychosocial management. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(1):77–93. - PubMed
-
- Mah JK, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2014;24(6):482–491. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Jr, Kunkel LM. Dystrophin: The protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987;51(6):919–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1RR031988/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR026139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD053177/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR062380/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000075/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P50AR060836/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD040677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR062380/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R24HD050846/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2U54HD053177/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD053177/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031988/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD040677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR026139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050846/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AR052646/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR061875/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR060836/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000075/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055100/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

