PEDF-derived peptide promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through its mitogenic effect on muscle progenitor cells
- PMID: 26040897
- PMCID: PMC4525084
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00344.2014
PEDF-derived peptide promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through its mitogenic effect on muscle progenitor cells
Abstract
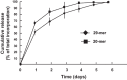
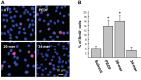
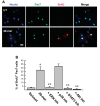
In response injury, intrinsic repair mechanisms are activated in skeletal muscle to replace the damaged muscle fibers with new muscle fibers. The regeneration process starts with the proliferation of satellite cells to give rise to myoblasts, which subsequently differentiate terminally into myofibers. Here, we investigated the promotion effect of pigment epithelial-derived factor (PEDF) on muscle regeneration. We report that PEDF and a synthetic PEDF-derived short peptide (PSP; residues Ser(93)-Leu(112)) induce satellite cell proliferation in vitro and promote muscle regeneration in vivo. Extensively, soleus muscle necrosis was induced in rats by bupivacaine, and an injectable alginate gel was used to release the PSP in the injured muscle. PSP delivery was found to stimulate satellite cell proliferation in damaged muscle and enhance the growth of regenerating myofibers, with complete regeneration of normal muscle mass by 2 wk. In cell culture, PEDF/PSP stimulated C2C12 myoblast proliferation, together with a rise in cyclin D1 expression. PEDF induced the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, Akt, and STAT3 in C2C12 myoblasts. Blocking the activity of ERK, Akt, or STAT3 with pharmacological inhibitors attenuated the effects of PEDF/PSP on the induction of C2C12 cell proliferation and cyclin D1 expression. Moreover, 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine pulse-labeling demonstrated that PEDF/PSP stimulated primary rat satellite cell proliferation in myofibers in vitro. In summary, we report for the first time that PSP is capable of promoting the regeneration of skeletal muscle. The signaling mechanism involves the ERK, AKT, and STAT3 pathways. These results show the potential utility of this PEDF peptide for muscle regeneration.
Keywords: myoblast; pigment epithelial-derived factor; satellite cell.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
PEDF-derived peptide promotes tendon regeneration through its mitogenic effect on tendon stem/progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jan 3;10(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1110-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30606221 Free PMC article.
-
PEDF promotes self-renewal of limbal stem cell and accelerates corneal epithelial wound healing.Stem Cells. 2013 Sep;31(9):1775-84. doi: 10.1002/stem.1393. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23553951
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor peptide promotes limbal stem cell proliferation through hedgehog pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jul;23(7):4759-4769. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14364. Epub 2019 May 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31066230 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-1 is a novel factor that regulates myotube growth in regenerating skeletal muscles.Curr Drug Targets. 2005 Jun;6(4):395-405. doi: 10.2174/1389450054021918. Curr Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 16026258 Review.
-
Prostaglandins in muscle regeneration.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2008;29(6-8):163-7. doi: 10.1007/s10974-008-9154-9. Epub 2008 Dec 4. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2008. PMID: 19052883 Review.
Cited by
-
Negative elongation factor regulates muscle progenitor expansion for efficient myofiber repair and stem cell pool repopulation.Dev Cell. 2021 Apr 5;56(7):1014-1029.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.025. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 33735618 Free PMC article.
-
Current Methods for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Repair and Regeneration.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Apr 16;2018:1984879. doi: 10.1155/2018/1984879. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29850487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor short peptides facilitate full-thickness cutaneous wound healing by promoting epithelial basal cell and hair follicle stem cell proliferation.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4853-4861. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5134. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29201190 Free PMC article.
-
Decellularized Diaphragmatic Muscle Drives a Constructive Angiogenic Response In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 28;19(5):1319. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051319. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29710813 Free PMC article.
-
PEDF-derived peptide promotes tendon regeneration through its mitogenic effect on tendon stem/progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jan 3;10(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1110-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30606221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnard W, Bower J, Brown MA, Murphy M, Austin L. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) infusion stimulates skeletal muscle regeneration after injury: injured muscle expresses lif mRNA. J Neurol Sci 123: 108–113, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Beitzel F, Sillence MN, Lynch GS. beta-Adrenoceptor signaling in regenerating skeletal muscle after beta-agonist administration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293: E932–E940, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bentzinger CF, Barzaghi P, Lin S, Ruegg MA. Overexpression of mini-agrin in skeletal muscle increases muscle integrity and regenerative capacity in laminin-alpha2-deficient mice. FASEB J 19: 934–942, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

