Discovery and characterization of novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase
- PMID: 26040985
- PMCID: PMC4603696
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10043
Discovery and characterization of novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase
Abstract
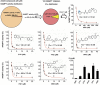
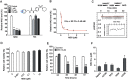
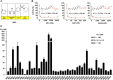
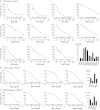
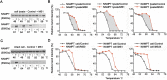
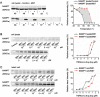
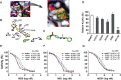
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) is a promising anticancer target. Using high throughput screening system targeting NAMPT, we obtained a potent NAMPT inhibitor MS0 (China Patent ZL201110447488.9) with excellent in vitro activity (IC50 = 9.87 ± 1.15 nM) and anti-proliferative activity against multiple human cancer cell lines including stem-like cancer cells. Structure-activity relationship studies yielded several highly effective analogues. These inhibitors specifically bound NAMPT, rather than downstream NMNAT. We provided the first chemical case using cellular thermal shift assay to explain the difference between in vitro and cellular activity; MS7 showed best in vitro activity (IC50 = 0.93 ± 0.29 nM) but worst cellular activity due to poor target engagement in living cells. Site-directed mutagenesis studies identified important residues for NAMPT catalytic activity and inhibitor binding. The present findings contribute to deep understanding the action mode of NAMPT inhibitors and future development of NAMPT inhibitors as anticancer agents.
Figures
References
-
- Dahl T. B., Holm S., Aukrust P. & Halvorsen B. Visfatin/NAMPT: a multifaceted molecule with diverse roles in physiology and pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 32, 229–243 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Miao C. Y. Introduction: Adipokines and cardiovascular disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 38, 860–863 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wang P., Vanhoutte P. M. & Miao C. Y. Visfatin and cardio-cerebro-vascular disease. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 59, 1–9 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Buldak R. J. et al. Visfatin affects redox adaptative responses and proliferation in Me45 human malignant melanoma cells: an in vitro study. Oncol. Rep. 29, 771–778 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Hasmann M. & Schemainda I. FK866, a highly specific noncompetitive inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, represents a novel mechanism for induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63, 7436–7442 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

