Preclinical development of HIvax: Human survivin highly immunogenic vaccines
- PMID: 26042612
- PMCID: PMC4514257
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1050572
Preclinical development of HIvax: Human survivin highly immunogenic vaccines
Abstract
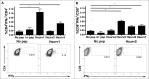
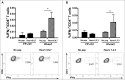
Our previous work involved the development of a recombinant fowlpox virus encoding survivin (FP-surv) vaccine that was evaluated for efficacy in mesothelioma mouse models. Results showed that FP-surv vaccination generated significant immune responses, which led to delayed tumor growth and improved animal survival. We have extended those previous findings in the current study, which involves the pre-clinical development of an optimized version of FP-surv designed for human immunization (HIvax). Survivin-derived peptides for the most common haplotypes in the human population were identified and their immunogenicity confirmed in co-culture experiments using dendritic cells and T cells isolated from healthy donors. Peptides confirmed to induce CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells activation in humans were then included in 2 transgenes optimized for presentation of processed peptides on MHC-I (HIvax1) and MHC-II (HIvax2). Fowlpox vectors expressing the HIvax transgenes were then generated and their efficacy was evaluated with subsequent co-culture experiments to measure interferon-γ and granzyme B secretion. In these experiments, both antigen specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells were activated by HIvax vaccines with resultant cytotoxic activity against survivin-overexpressing mesothelioma cancer cells. These results provide a rationale for clinical testing of HIvax1 and HIvax2 vaccines in patients with survivin-expressing cancers.
Keywords: EpiMatrix; T-Lymphocytes; cancer vaccines; fowlpox; immunodominant epitopes; mesothelioma; tregitopes.
Figures



References
-
- Melief CJ, Kast WM. T-cell immunotherapy of tumors by adoptive transfer of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and by vaccination with minimal essential epitopes. Immunol Rev 1995; 145:167-77; PMID:7590825; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.1995.tb00081.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hung K, Hayashi R, Lafond-Walker A, Lowenstein C, Pardoll D, Levitsky H. The central role of CD4(+) T cells in the antitumor immune response. J Exp Med 1998; 188:2357-68; PMID:9858522; http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.188.12.2357. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Elisseeva OA, Nakajima H, Fujiki F, Kawakami M, Shirakata T, Nishida S, Hosen N, Oji Y, et al.. WT1 peptide cancer vaccine for patients with hematopoietic malignancies and solid cancers. Sci World J 2007; 7:649-65; PMID:17619750; http://dx.doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2007.119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hazama S, Nakamura Y, Takenouchi H, Suzuki N, Tsunedomi R, Inoue Y, Tokuhisa Y, Iizuka N, Yoshino S, Takeda K, et al.. A phase I study of combination vaccine treatment of five therapeutic epitope-peptides for metastatic colorectal cancer; safety, immunological response, and clinical outcome. J Transl Med 2014; 12:63; PMID:24612787; http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-12-63. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lennerz V, Gross S, Gallerani E, Sessa C, Mach N, Boehm S, Hess D, von Boehmer L, Knuth A, Ochsenbein AF, et al.. Immunologic response to the survivin-derived multi-epitope vaccine EMD640744 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2014; 63:381-94; PMID:24487961; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1516-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
