Trypanothione reductase: a target protein for a combined in vitro and in silico screening approach
- PMID: 26042772
- PMCID: PMC4456413
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003773
Trypanothione reductase: a target protein for a combined in vitro and in silico screening approach
Abstract
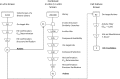
With the goal to identify novel trypanothione reductase (TR) inhibitors, we performed a combination of in vitro and in silico screening approaches. Starting from a highly diverse compound set of 2,816 compounds, 21 novel TR inhibiting compounds could be identified in the initial in vitro screening campaign against T. cruzi TR. All 21 in vitro hits were used in a subsequent similarity search-based in silico screening on a database containing 200,000 physically available compounds. The similarity search resulted in a data set containing 1,204 potential TR inhibitors, which was subjected to a second in vitro screening campaign leading to 61 additional active compounds. This corresponds to an approximately 10-fold enrichment compared to the initial pure in vitro screening. In total, 82 novel TR inhibitors with activities down to the nM range could be identified proving the validity of our combined in vitro/in silico approach. Moreover, the four most active compounds, showing IC50 values of <1 μM, were selected for determining the inhibitor constant. In first on parasites assays, three compounds inhibited the proliferation of bloodstream T. brucei cell line 449 with EC50 values down to 2 μM.
Conflict of interest statement
MB, FO, SN, and PMS were at the time of the studies employed by MSD Animal Health Innovation GmbH in Schwabenheim, Zur Propstei, Germany. This does not alter our adherence to all PLOS NTDs policies on sharing data and materials. Other than the above, the authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Flohé L (2011) The trypanothione system and the opportunities it offers to create drugs for the neglected kinetoplast diseases. Biotechnol Advances 30: 294–301. - PubMed
-
- Ilemobade A.A., Tsetse and trypanosomosis in Africa: the challenges, the opportunities. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 2009. 76: 35–40. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Working to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases. Available from http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/2010report/en/ (2010). - PubMed
-
- Fairlamb AH (2013) Foreword. Drug Discovery for Neglected Diseases—Past and Present and Future In: Jäger T, Koch O, Flohé L, editors. Trypanosomatid Diseases, Molecular Routes to Drug Discovery. Weinheim: Wiley-Blackwell, IX p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

