Simvastatin Suppresses Airway IL-17 and Upregulates IL-10 in Patients With Stable COPD
- PMID: 26043025
- PMCID: PMC4631035
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.14-3138
Simvastatin Suppresses Airway IL-17 and Upregulates IL-10 in Patients With Stable COPD
Abstract
Background: Statins have immunomodulatory properties that may provide beneficial effects in the treatment of COPD. We investigated whether a statin improves the IL-17/IL-10 imbalance in patients with COPD, as has previously been demonstrated in patients with asthma.
Methods: Thirty patients with stable COPD were recruited to a double-blind, randomized, controlled, crossover trial comparing the effect of simvastatin, 20 mg po daily, with that of a matched placebo on sputum inflammatory markers and airway inflammation. Each treatment was administered for 4 weeks separated by a 4-week washout period. The primary outcome was the presence of T-helper 17 cytokines and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in induced sputum. Secondary outcomes included sputum inflammatory cells, FEV1, and symptoms using the COPD Assessment Test (CAT).
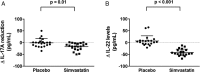
Results: At 4 weeks, there was a significant reduction in sputum IL-17A, IL-22, IL-6, and CXCL8 concentrations (mean difference, -16.4 pg/mL, P = .01; -48.6 pg/mL, P < .001; -45.3 pg/mL, P = .002; and -190.9 pg/mL, P = .007, respectively), whereas IL-10 concentrations, IDO messenger RNA expression (fold change), and IDO activity (kynurenine to tryptophan ratio) were markedly increased during simvastatin treatment compared with placebo treatment periods (mean difference, 24.7 pg/mL, P < .001; 1.02, P < .001; and 0.47, P < .001, respectively). The absolute sputum macrophage count, proportion of macrophages, and CAT score were reduced after simvastatin compared with placebo (mean difference, -0.16 × 106, P = .004; -14.1%, P < .001; and -3.2, P = .02, respectively). Values for other clinical outcomes were similar between the simvastatin and placebo treatments.
Conclusions: Simvastatin reversed the IL-17A/IL-10 imbalance in the airways and reduced sputum macrophage but not neutrophil counts in patients with COPD.
Trial registry: ClinicalTrials.gov; No.: NCT01944176; www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Figures



References
-
- Alcorn JF, Crowe CR, Kolls JK. TH17 cells in asthma and COPD. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;72:495-516. - PubMed
-
- Kolls JK, Lindén A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21(4):467-476. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Al-Alwan L, Audusseau S, et al. Genetic deletion of IL-17A reduces cigarette smoke-induced inflammation and alveolar type II cell apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014;306(2):L132-L143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

