T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) development and regulation of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 production
- PMID: 26044597
- PMCID: PMC4532589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.010
T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) development and regulation of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 production
Abstract
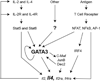
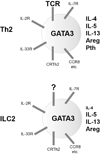
Interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5 and IL-13, the signature cytokines that are produced during type 2 immune responses, are critical for protective immunity against infections of extracellular parasites and are responsible for asthma and many other allergic inflammatory diseases. Although many immune cell types within the myeloid lineage compartment including basophils, eosinophils and mast cells are capable of producing at least one of these cytokines, the production of these "type 2 immune response-related" cytokines by lymphoid lineages, CD4 T helper 2 (Th2) cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in particular, are the central events during type 2 immune responses. In this review, I will focus on the signaling pathways and key molecules that determine the differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into Th2 cells, and how the expression of Th2 cytokines, especially IL-4 and IL-13, is regulated in Th2 cells. The similarities and differences in the differentiation of Th2 cells, IL-4-producing T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and ILC2s as well as their relationships will also be discussed.
Keywords: GATA3; Interleukin-13; Interleukin-4; Type 2 T helper cells (Th2); Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2).
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annual review of immunology. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
-
- Paul WE, Seder RA. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994;76:241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

