Optimal combination treatment and vascular outcomes in recent ischemic stroke patients by premorbid risk level
- PMID: 26044963
- PMCID: PMC4492833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.05.028
Optimal combination treatment and vascular outcomes in recent ischemic stroke patients by premorbid risk level
Abstract
Background: Optimal combination of secondary stroke prevention treatment including antihypertensives, antithrombotic agents, and lipid modifiers is associated with reduced recurrent vascular risk including stroke. It is unclear whether optimal combination treatment has a differential impact on stroke patients based on level of vascular risk.
Methods: We analyzed a clinical trial dataset comprising 3680 recent non-cardioembolic stroke patients aged ≥35 years and followed for 2 years. Patients were categorized by appropriateness levels 0 to III depending on the number of the drugs prescribed divided by the number of drugs potentially indicated for each patient (0=none of the indicated medications prescribed and III=all indicated medications prescribed [optimal combination treatment]). High-risk was defined as having a history of stroke or coronary heart disease (CHD) prior to the index stroke event. Independent associations of medication appropriateness level with a major vascular event (stroke, CHD, or vascular death), ischemic stroke, and all-cause death were analyzed.
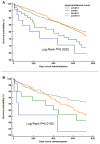
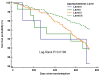
Results: Compared with level 0, for major vascular events, the HR of level III in the low-risk group was 0.51 (95% CI: 0.20-1.28) and 0.32 (0.14-0.70) in the high-risk group; for stroke, the HR of level III in the low-risk group was 0.54 (0.16-1.77) and 0.25 (0.08-0.85) in the high-risk group; and for all-cause death, the HR of level III in the low-risk group was 0.66 (0.09-5.00) and 0.22 (0.06-0.78) in the high-risk group.
Conclusion: Optimal combination treatment is related to a significantly lower risk of future vascular events and death among high-risk patients after a recent non-cardioembolic stroke.
Keywords: Death; Drug; High-risk; Secondary prevention; Stroke; Vascular events.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Gu Q, Burt VL, Dillon CF, Yoon S. Trends in antihypertensive medication use and blood pressure control among United States adults with hypertension: the National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001 to 2010. Circulation. 2012;126:2105–14. - PubMed
-
- Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2160–236. - PubMed
-
- Toole JF, Malinow MR, Chambless LE, Spence JD, Pettigrew LC, Howard VJ, et al. Lowering homocysteine in patients with ischemic stroke to prevent recurrent stroke, myocardial infarction, and death: the Vitamin Intervention for Stroke Prevention (VISP) randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291:565–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

