A comprehensive long-term prognosis of chronic hepatitis C patients with antiviral therapy: a meta-analysis of studies from 2008 to 2014
- PMID: 26045707
- PMCID: PMC4451277
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.15(5)2015.27181
A comprehensive long-term prognosis of chronic hepatitis C patients with antiviral therapy: a meta-analysis of studies from 2008 to 2014
Abstract
Context: Attaining a sustained virological response with antiviral therapy is a sign of clinical cure for chronic hepatitis C patients. The aim of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the long-term efficiency and outcome of antiviral therapy in patients with hepatitis C who attained a sustained virological response.
Evidence acquisition: A literature search was performed on published articles between January 2008 and February 2014. Patients with Hepatitis C who received interferon with or without ribavirin therapy were enrolled. Relative risks were estimated using either fixed or random effect models.
Results: Patients who attained sustained virological response had a less risk (85%) for all-cause mortality and about 63% reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma incidence than those who did not achieve sustained virological response. Based on deeply analysis, the stage of liver fibrosis was a risk factor at baseline for the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conclusions: Sustained virological response can reduce all-cause mortality and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma of patients with hepatitis C. Advanced liver fibrosis is still a risk factor for the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, in spite of hepatitis C patients attained a sustained virological response.
Keywords: Antiviral Therapy; Chronic Hepatitis C; Meta-Analysis.
Figures
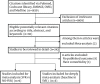



References
-
- Lavanchy D. Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(2):107–15. - PubMed
-
- Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis C. . Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2009;29(Suppl 1):74–81. - PubMed
-
- Farci P. Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome [Science 1989;244:359-362]. J Hepatol. 2002;36(5):582–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
