Toxoplasmosis presented as a submental mass: a common disease, uncommon presentation
- PMID: 26045858
- PMCID: PMC4440167
Toxoplasmosis presented as a submental mass: a common disease, uncommon presentation
Abstract
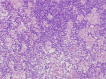
Submental mass secondary to toxoplasmosis is not common in clinical work. A diagnosis of toxoplasmosis is rarely considered by physicians. Here we describe a 50-year-old woman presented with a progressive, painful, submental and left neck swelling for 1 month. After having obtained an insufficient evidence from the fine-needle biopsy, the patient finally received an excisional biopsy which highly indicated the possibility of lymphadenopathy consistent with toxoplasmosis. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis was finally established by a combination of the pathological criteria, together with the positive serological finding. According to review the clinical presentations, pathological characteristics, diagnostic standard and treatment of this disease, the article aims to remind otolaryngologists who are evaluating a neck mass should be aware of the infectious cause of lymphadenopathy and the possibility of toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Toxoplasmosis; diagnosis; lymphadenopathy; toxoplasma.
Figures
References
-
- Montoya JG, liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 2004;363:1965–1976. - PubMed
-
- Jones JL, Kruszon-Moran D, Sanders-Lewis K, Wilson M. Toxoplasma gondii infection in the United States, decline from the prior decade. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77:405–410. - PubMed
-
- Hadi U, Rameh C. Intraglandular toxoplasmosis of the parotid gland pre- or postoperative diagnosis? Am J Otolaryngol. 2007;28:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Shashy RG, Pinhero D, Kerry D. Toxoplasmosis lymphadenitis presenting as a parotid mass: a report of 2 cases. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006;85:666–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical