The nuclear pore complex--structure and function at a glance
- PMID: 26046137
- PMCID: PMC4311126
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.083246
The nuclear pore complex--structure and function at a glance
Abstract
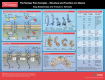
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are indispensable for cell function and are at the center of several human diseases. NPCs provide access to the nucleus and regulate the transport of proteins and RNA across the nuclear envelope. They are aqueous channels generated from a complex network of evolutionarily conserved proteins known as nucleporins. In this Cell Science at a Glance article and the accompanying poster, we discuss how transport between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm is regulated, what we currently know about the structure of individual nucleoporins and the assembled NPC, and how the cell regulates assembly and disassembly of such a massive structure. Our aim is to provide a general overview on what we currently know about the nuclear pore and point out directions of research this area is heading to.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources