Intragingival injection of Porphyromonas gingivalis-derived lipopolysaccharide induces a transient increase in gingival tumour necrosis factor-α, but not interleukin-6, in anaesthetised rats
- PMID: 26047579
- PMCID: PMC4582562
- DOI: 10.1038/ijos.2015.9
Intragingival injection of Porphyromonas gingivalis-derived lipopolysaccharide induces a transient increase in gingival tumour necrosis factor-α, but not interleukin-6, in anaesthetised rats
Abstract
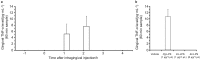
This study used in vivo microdialysis to examine the effects of intragingival application of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg-LPS) on gingival tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 levels in rats. A microdialysis probe with an injection needle attached to the surface of the dialysis membrane was implanted into the gingiva of the upper incisor. For comparison, the effects of LPS derived from Escherichia coli (Ec-LPS) on IL-6 and TNF-α levels were also analysed. Pg-LPS (1 μg/1 μL) or Ec-LPS (1 or 6 μg/1 μL) was applied by microsyringe, with gingival dialysates collected every hour. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) revealed that gingival dialysates contained approximately 389 pg·mL⁻¹ of IL-6 basally; basal TNF-α levels were lower than the detection limit of the ELISA. Pg-LPS failed to alter IL-6 levels but markedly increased TNF-α levels, which remained elevated for 2 h after treatment. Neither IL-6 nor TNF-α were affected by Ec-LPS. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis revealed that the gingiva expresses Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 mRNA. Immunohistochemical examination showed that TLR2 and TLR4 are expressed by gingival epithelial cells. The present study provides in vivo evidence that locally applied Pg-LPS, but not Ec-LPS, into the gingiva transiently increases gingival TNF-α without affecting IL-6. The present results suggest that TLR2 but not TLR4 expressed on gingival epithelial cells may mediate the Pg-LPS-induced increase in gingival TNF-α in rats.
Figures




References
-
- 1Page RC. The role of inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res 1991; 26(3 Pt 2): 230–242. - PubMed
-
- 2Slots J. Periodontology: past, present, perspectives. Periodontol 2000 2013; 62(1): 7–19. - PubMed
-
- 3Wilson M. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharides from oral bacteria and their relevance to the pathogenesis of chronic periodontitis. Sci Prog 1995; 78(Pt 1): 19–34. - PubMed
-
- 4Nakai K, Kawato T, Morita T et al. Angiotensin II induces the production of MMP-3 and MMP-13 through the MAPK signaling pathways via the AT(1) receptor in osteoblasts. Biochimie 2013; 95(4): 922–933. - PubMed
-
- 5de Aquino SG, Guimaraes MR, Stach-Machado DR et al. Differential regulation of MMP-13 expression in two models of experimentally induced periodontal disease in rats. Arch Oral Biol 2009; 54(7): 609–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

