Rasch Analysis of the Wrist and Hand Fugl-Meyer: Dimensionality and Item-Level Characteristics
- PMID: 26050075
- PMCID: PMC4470757
- DOI: 10.1097/NPT.0000000000000096
Rasch Analysis of the Wrist and Hand Fugl-Meyer: Dimensionality and Item-Level Characteristics
Abstract
Background and purpose: Clinical administration of the wrist stability, wrist mobility, and hand items of the upper-extremity Fugl-Meyer (W/H UE FM) may provide a rigorous, easily administered, bedside measure of motor impairment in mildly impaired stroke survivors. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the item structure of the W/H UE FM to better understand its measurement properties using Rasch analysis.
Methods: This was a secondary analysis of W/H UE FM data arising from clinical trials of mildly impaired stroke survivors using latent parallel analysis, ordinal factor analysis, and partial credit model Rasch analyses.
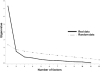
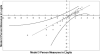
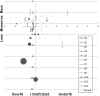
Results: Latent parallel analysis and ordinal factor analysis indicated that all W/H UE FM items represent a single unidimensional construct, wrist and hand motor ability. Rasch analysis of data from 150 mildly impaired stroke survivors (94 men; mean age, 57.1 ± 11.4 years; mean time since stroke, 19.5 months) revealed that the W/H UE FM operated as a reliable, valid, and effective measure of wrist and hand motor ability. These data were compatible with Rasch model assumptions and are consistent with previous W/H UE FM research. Mass flexion and extension movements were the least difficult W/H UE FM items while the radial and hook grasp items were the most difficult.
Discussion and conclusion: The W/H UE FM is well suited to mildly impaired stroke survivors who exhibit the ability to perform mass flexion and mass extension movements. The full-scale UE FM may be preferable for stroke survivors with lower levels of ability.Video abstract available for additional insight from the authors (Supplemental Digital Content 1, http://links.lww.com/JNPT/A108).
Figures
References
-
- Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser A, Kase CS, Scaramucci A, D'Agostino RB, Wolf PA. The influence of gender and age on disability following ischemic stroke: The framingham study. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2003;12:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Gresham GE, Fitzpatrick TE, Wolf PA, McNamara PM, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. Residual disability in survivors of stroke--the framingham study. N Engl J Med. 1975;293:954–6. - PubMed
-
- Fugl-Meyer AR, Jääskö L, Leyman I, Olsson S, Steglind S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient: A method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1975;7:13–31. - PubMed
-
- Woodbury ML, Velozo CA, Richards LG, Duncan PW. Rasch analysis staging methodology to classify upper extremity movement impairment after stroke. YAPMR Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2013;94:1527–1533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

