Hijacking the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cereblon to Efficiently Target BRD4
- PMID: 26051217
- PMCID: PMC4475452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.05.009
Hijacking the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cereblon to Efficiently Target BRD4
Abstract
BRD4, a bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family member, is an attractive target in multiple pathological settings, particularly cancer. While BRD4 inhibitors have shown some promise in MYC-driven malignancies such as Burkitt's lymphoma (BL), we show that BRD4 inhibitors lead to robust BRD4 protein accumulation, which may account for their limited suppression of MYC expression, modest antiproliferative activity, and lack of apoptotic induction. To address these limitations we designed ARV-825, a hetero-bifunctional PROTAC (Proteolysis Targeting Chimera) that recruits BRD4 to the E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon, leading to fast, efficient, and prolonged degradation of BRD4 in all BL cell lines tested. Consequently, ARV-825 more effectively suppresses c-MYC levels and downstream signaling than small-molecule BRD4 inhibitors, resulting in more effective cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction in BL. Our findings provide strong evidence that cereblon-based PROTACs provide a better and more efficient strategy in targeting BRD4 than traditional small-molecule inhibitors.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


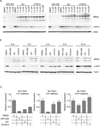
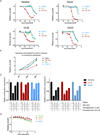
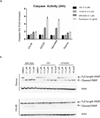
Comment in
-
Protein-slaying drugs could be the next blockbuster therapies.Nature. 2019 Mar;567(7748):298-300. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-00879-3. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30894734 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baratta MG, Schinzel AC, Zwang Y, Bandopadhayay P, Bowman-Colin C, Kutt J, Curtis J, Piao H, Wong LC, Kung AL, et al. An in-tumor genetic screen reveals that the BET bromodomain protein, BRD4, is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2015;112:232–237. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boi M, Gaudio E, Bonetti P, Kwee I, Bernasconi E, Tarantelli C, Rinaldi A, Testoni M, Cascione L, Ponzoni M, et al. The BET Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 affects pathogenetic pathways in pre-clinical B-cell tumor models and synergizes with targeted drugs. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

