Class I histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit the retention of BRCA1 and 53BP1 at the site of DNA damage
- PMID: 26053117
- PMCID: PMC4556395
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12717
Class I histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit the retention of BRCA1 and 53BP1 at the site of DNA damage
Abstract
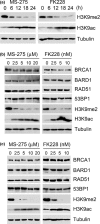
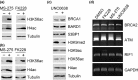
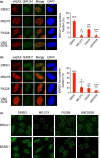
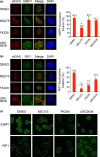
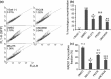
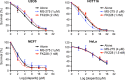
BRCA1 and 53BP1 antagonistically regulate homology-directed repair (HDR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) of DNA double-strand breaks (DSB). The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor trichostatin A directly inhibits the retention of 53BP1 at DSB sites by acetylating histone H4 (H4ac), which interferes with 53BP1 binding to dimethylated histone H4 Lys20 (H4K20me2). Conversely, we recently found that the retention of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex is also affected by another methylated histone residue, H3K9me2, which can be suppressed by the histone lysine methyltransferase (HKMT) inhibitor UNC0638. Here, we investigate the effects of the class I HDAC inhibitors MS-275 and FK228 compared to UNC0638 on histone modifications and the DNA damage response. In addition to H4ac, the HDAC inhibitors induce H3K9ac and inhibit H3K9me2 at doses that do not affect the expression levels of DNA repair genes. By contrast, UNC0638 selectively inhibits H3K9me2 without affecting the levels of H3K9ac, H3K56ac or H4ac. Reflecting their effects on histone modifications, the HDAC inhibitors inhibit ionizing radiation-induced foci (IRIF) formation of BRCA1 and BARD1 as well as 53BP1 and RIF1, whereas UNC0638 suppresses IRIF formation of BRCA1 and BARD1 but not 53BP1 and RIF1. Although HDAC inhibitors suppressed HDR, they did not cooperate with the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib to block cancer cell growth, possibly due to simultaneous suppression of NHEJ pathway components. Collectively, these results suggest the mechanism by that HDAC inhibitors inhibit both the HDR and NHEJ pathways, whereas HKMT inhibitor inhibits only the HDR pathway; this finding may affect the chemosensitizing effects of the inhibitors.
Keywords: 53BP1; BRCA1; DNA damage response; histone deacetylase inhibitor; histone modifications.
© 2015 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Hsiao K-Y, Mizzen CA. Histone H4 deacetylation facilitates 53BP1 DNA damage signaling and double-strand break repair. J Mol Cell Biol. 2013;5:157–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

