HDL-bound sphingosine-1-phosphate restrains lymphopoiesis and neuroinflammation
- PMID: 26053123
- PMCID: PMC4506268
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14462
HDL-bound sphingosine-1-phosphate restrains lymphopoiesis and neuroinflammation
Abstract
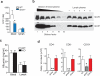
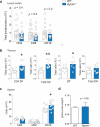
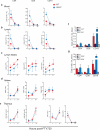
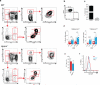
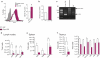
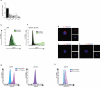
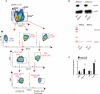
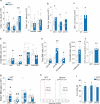
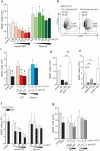
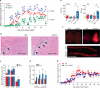
Lipid mediators influence immunity in myriad ways. For example, circulating sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a key regulator of lymphocyte egress. Although the majority of plasma S1P is bound to apolipoprotein M (ApoM) in the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particle, the immunological functions of the ApoM-S1P complex are unknown. Here we show that ApoM-S1P is dispensable for lymphocyte trafficking yet restrains lymphopoiesis by activating the S1P1 receptor on bone marrow lymphocyte progenitors. Mice that lacked ApoM (Apom(-/-)) had increased proliferation of Lin(-) Sca-1(+) cKit(+) haematopoietic progenitor cells (LSKs) and common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) in bone marrow. Pharmacological activation or genetic overexpression of S1P1 suppressed LSK and CLP cell proliferation in vivo. ApoM was stably associated with bone marrow CLPs, which showed active S1P1 signalling in vivo. Moreover, ApoM-bound S1P, but not albumin-bound S1P, inhibited lymphopoiesis in vitro. Upon immune stimulation, Apom(-/-) mice developed more severe experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, characterized by increased lymphocytes in the central nervous system and breakdown of the blood-brain barrier. Thus, the ApoM-S1P-S1P1 signalling axis restrains the lymphocyte compartment and, subsequently, adaptive immune responses. Unique biological functions imparted by specific S1P chaperones could be exploited for novel therapeutic opportunities.
Figures

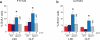

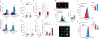
References
-
- Cyster JG, Schwab SR. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012;30:69–94. - PubMed
-
- Schwab SR, et al. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science. 2005;309:1735–1739. - PubMed
-
- Furlan R, Cuomo C, Martino G. Animal models of multiple sclerosis. Methods Mo.l Biol. 2009;549:157–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 CA142117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA14211/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DK056014/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HL89934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL70694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DK056015/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA138313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL067330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DC014211/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- HL67330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017677/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

