The Efficacy and Clinical Safety of Various Analgesic Combinations for Post-Operative Pain after Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26053953
- PMCID: PMC4459961
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127611
The Efficacy and Clinical Safety of Various Analgesic Combinations for Post-Operative Pain after Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To run a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials aiming to answer the clinical question "which analgesic combination and dosage is potentially the most effective and safe for acute post-operative pain control after third molar surgery?".
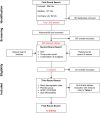
Materials and methods: A systematic search of computer databases and journals was performed. The search and the evaluations of articles were performed by 2 independent reviewers in 3 rounds. Randomized clinical trials related to analgesic combinations for acute post-operative pain control after lower third molar surgery that matched the selection criteria were evaluated to enter in the final review.
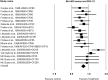
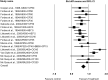
Results: Fourteen studies with 3521 subjects, with 10 groups (17 dosages) of analgesic combinations were included in the final review. The analgesic efficacy were presented by the objective pain measurements including sum of pain intensity at 6 hours (SPID6) and total pain relief at 6 hours (TOTPAR6). The SPID6 scores and TOTPAR6 scores of the reported analgesic combinations were ranged from 1.46 to 6.44 and 3.24 - 10.3, respectively. Ibuprofen 400mg with oxycodone HCL 5mg had superior efficacy (SPID6: 6.44, TOTPAR6: 9.31). Nausea was the most common adverse effect, with prevalence ranging from 0-55%. Ibuprofen 200mg with caffeine 100mg or 200mg had a reasonable analgesic effect with fewer side effects.
Conclusion: This systematic review and meta-analysis may help clinicians in their choices of prescribing an analgesic combination for acute post-operative pain control after lower third molar surgery. It was found in this systematic review Ibuprofen 400mg combined with oxycodone HCL 5mg has superior analgesic efficacy when compared to the other analgesic combinations included in this study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ibuprofen and/or paracetamol (acetaminophen) for pain relief after surgical removal of lower wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 12;2013(12):CD004624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004624.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24338830 Free PMC article.
-
Single dose oral analgesics for acute postoperative pain in adults - an overview of Cochrane reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 28;2015(9):CD008659. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008659.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26414123 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Non-prescription (OTC) oral analgesics for acute pain - an overview of Cochrane reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 4;2015(11):CD010794. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010794.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26544675 Free PMC article.
-
Single dose oral analgesics for acute postoperative pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Sep 7;(9):CD008659. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008659.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 28;(9):CD008659. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008659.pub3. PMID: 21901726 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Application of sequential multimodal analgesia before and after impacted mandibular third molar extraction: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2023 Jan 18;32:101078. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101078. eCollection 2023 Apr. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2023. PMID: 36762120 Free PMC article.
-
New quantitative classification of the anatomical relationship between impacted third molars and the inferior alveolar nerve.BMC Med Imaging. 2015 Dec 7;15:59. doi: 10.1186/s12880-015-0101-0. BMC Med Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26643322 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a Single Dose of Deflazacort on Postoperative Pain, Swelling, and Trismus after Impacted Lower Third Molar Surgery: Randomised Clinical Trial.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jul 25;60(8):1206. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081206. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202488 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Opioid Analgesic Reduction Study (OARS)-a comparison of opioid vs. non-opioid combination analgesics for management of post-surgical pain: a double-blind randomized clinical trial.Trials. 2022 Feb 17;23(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06064-8. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35177108 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Chlorhexidine after Oral Surgery Procedures on Wound Healing: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;12(10):1552. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12101552. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A M, I P. Perioperative NSAIDs: towards greater safety. Pain Rev. 1995;2:268–91.
-
- Romsing J, Moiniche S, Dahl JB. Rectal and parenteral paracetamol, and paracetamol in combination with NSAIDs, for postoperative analgesia. British journal of anaesthesia. 2002;88(2):215–26. Epub 2002/03/07. . - PubMed
-
- Raffa RB. Pharmacology of oral combination analgesics: rational therapy of pain. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2001;26:257–64. - PubMed
-
- Besson JM. The neurobiology of pain. Lancet. 1999;353(9164):1610–5. Epub 1999/05/20. . - PubMed
-
- Schug SA, Zech D, Dorr U. Cancer pain management according to WHO analgesic guidelines. Journal of pain and symptom management. 1990;5(1):27–32. Epub 1990/02/01. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources