Complement regulator CD46: genetic variants and disease associations
- PMID: 26054645
- PMCID: PMC4469999
- DOI: 10.1186/s40246-015-0029-z
Complement regulator CD46: genetic variants and disease associations
Abstract
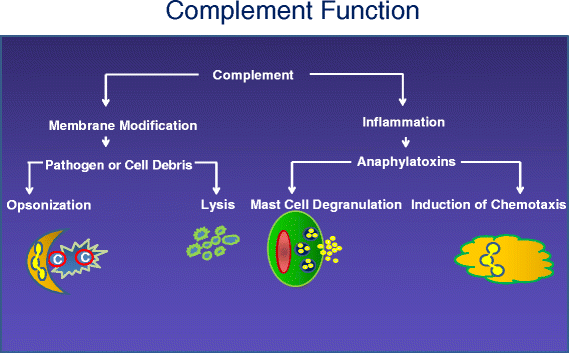
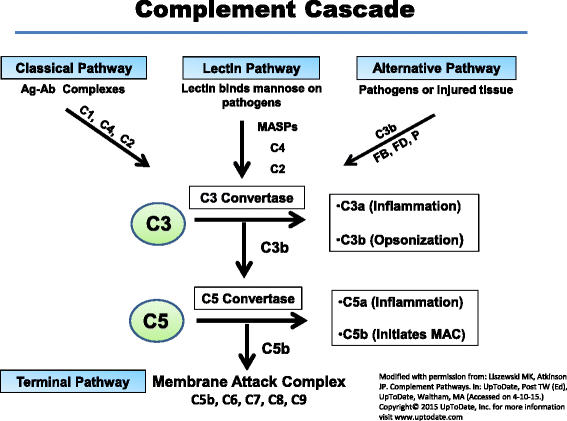
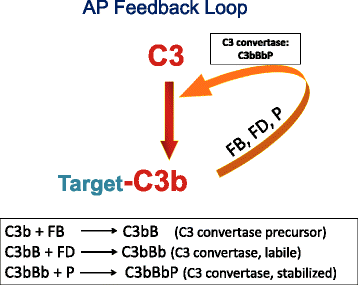
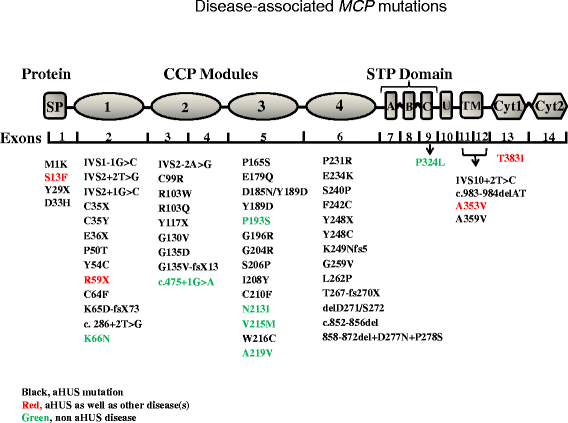
Membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46) is an ubiquitously expressed complement regulatory protein that protects host cells from injury by complement. This type-I membrane glycoprotein serves as a cofactor for the serine protease factor I to mediate inactivation of C3b and C4b deposited on host cells. More than 60 disease-associated mutations in MCP have now been identified. The majority of the mutations are linked to a rare thrombotic microangiopathic-based disease, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), but new putative links to systemic lupus erythematosus, glomerulonephritis, and pregnancy-related disorders among others have also been identified. This review summarizes our current knowledge of disease-associated mutations in this complement inhibitor.
Figures

References
-
- Ariki S, Takahara S, Shibata T, Fukuoka T, Ozaki A, Endo Y, et al. Factor C acts as a lipopolysaccharide-responsive C3 convertase in horseshoe crab complement activation. J Immunol. 2008;181 (11):7994–8001. doi:181/11/7994. - PubMed
-
- Pettigrew HD, Teuber SS, Gershwin ME. Clinical significance of complement deficiencies. In: Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME, editors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Boston: Blackwell Publishing; 2009. pp. 108–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

