Early chronic kidney disease: diagnosis, management and models of care
- PMID: 26055354
- PMCID: PMC4531835
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.85
Early chronic kidney disease: diagnosis, management and models of care
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is prevalent in many countries, and the costs associated with the care of patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are estimated to exceed US$1 trillion globally. The clinical and economic rationale for the design of timely and appropriate health system responses to limit the progression of CKD to ESRD is clear. Clinical care might improve if early-stage CKD with risk of progression to ESRD is differentiated from early-stage CKD that is unlikely to advance. The diagnostic tests that are currently used for CKD exhibit key limitations; therefore, additional research is required to increase awareness of the risk factors for CKD progression. Systems modelling can be used to evaluate the impact of different care models on CKD outcomes and costs. The US Indian Health Service has demonstrated that an integrated, system-wide approach can produce notable benefits on cardiovascular and renal health outcomes. Economic and clinical improvements might, therefore, be possible if CKD is reconceptualized as a part of primary care. This Review discusses which early CKD interventions are appropriate, the optimum time to provide clinical care, and the most suitable model of care to adopt.
Figures

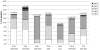
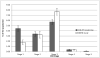

References
-
- James MT, Hemmelgarn BR, Tonelli M. Early recognition and prevention of chronic kidney disease (vol 375, pg 1296, 2010) Lancet. 2010;376:162–162. - PubMed
-
- Sarnak MJ, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease - A statement from the American Heart Association councils on kidney in cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure research, clinical cardiology, and epidemiology and prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease - Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney International Supplement. 2013;3:150. - PubMed
-
- Chen RA, Scott S, Mattern WD, Mohini R, Nissenson AR. The case for disease management in chronic kidney disease. Dis Manag. 2006;9:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2012;379:165–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

